在Android開發中,我們常常會遇到流布式的布局,常常會用來1些標簽的顯示,比如qq中個人便簽,搜索框下方提示的詞語,這些是指都是流布式的布局,今天我就我們平常開放中遇到的流布式布局坐1些總結
轉載請注明博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/51765428
源碼下載地址:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/CustomViewDemo.git
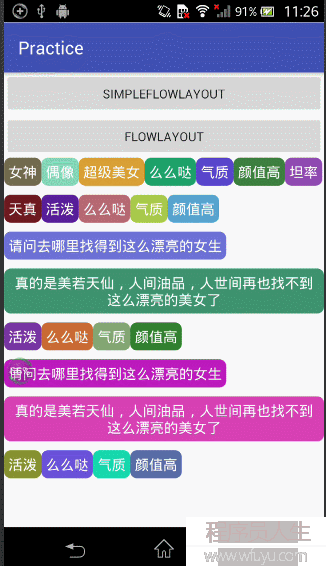

仔細視察,我們可以知道圖2實際上是圖1效果的升級版,圖1當我們控件的寬度超過這1行的時候,剩余的寬度它不會自動散布到每一個控件中,而圖2的效果當我們換行的時候,如控件還沒有占滿這1行的時候,它會自動把剩余的寬度散布到每一個控件中
`
/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu
* @author xujun
* @time 2016/6/20 23:49.
*/
public class SimpleFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int verticalSpacing = 20;
public SimpleFlowLayout(Context context ) {
super(context);
}
/**
* 重寫onMeasure方法是為了肯定終究的大小
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
//處理Padding屬性,讓當前的ViewGroup支持Padding
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int heightUsed = paddingTop + paddingBottom;
int childMaxHeightOfThisLine = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 已用的寬度
int childUsedWidth = 0;
// 已用的高度
int childUsedHeight = 0;
// 調用ViewGroup本身的方法丈量孩子的寬度和高度,我們也能夠自己根據MeasureMode來丈量
measureChild(child,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
childUsedWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth();
childUsedHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight();
//處理Margin,支持孩子的Margin屬性
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childUsedWidth += leftMargin + rightMargin;
childUsedHeight += topMargin + bottomMargin;
//總寬度沒有超過本行
if (widthUsed + childUsedWidth < widthSpecSize) {
widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) {
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
} else {//總寬度已超過本行
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine + verticalSpacing;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight + childUsedWidth;
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
}
}
//加上最后1行的最大高度
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine;
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightUsed);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
/**
* 為了 支持Padding屬性
*/
int childStartLayoutX = paddingLeft;
int childStartLayoutY = paddingTop;
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int childMaxHeight = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
//擺放每個孩子的高度
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
int childNeededWidth, childNeedHeight;
int left, top, right, bottom;
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childMeasuredHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childNeededWidth = leftMargin + rightMargin + childMeasuredWidth;
childNeedHeight = topMargin + topMargin + childMeasuredHeight;
// 沒有超過本行
if (widthUsed + childNeededWidth <= r - l) {
if (childNeedHeight > childMaxHeight) {
childMaxHeight = childNeedHeight;
}
left = childStartLayoutX + leftMargin;
top = childStartLayoutY + topMargin;
right = left + childMeasuredWidth;
bottom = top + childMeasuredHeight;
widthUsed += childNeededWidth;
childStartLayoutX += childNeededWidth;
} else {
childStartLayoutY += childMaxHeight + verticalSpacing;
childStartLayoutX = paddingLeft;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
left = childStartLayoutX + leftMargin;
top = childStartLayoutY + topMargin;
right = left + childMeasuredWidth;
bottom = top + childMeasuredHeight;
widthUsed += childNeededWidth;
childStartLayoutX += childNeededWidth;
childMaxHeight = childNeedHeight;
}
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
private Rect getMarginRect(View child) {
LayoutParams layoutParams = child.getLayoutParams();
int leftMargin = 0;
int rightMargin = 0;
int topMargin = 0;
int bottomMargin = 0;
if (layoutParams instanceof MarginLayoutParams) {
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) layoutParams;
leftMargin = marginLayoutParams.leftMargin;
rightMargin = marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
topMargin = marginLayoutParams.topMargin;
bottomMargin = marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin;
}
return new Rect(leftMargin, topMargin, rightMargin, bottomMargin);
}
}`
添加完1個孩子以后我們判斷widthUsed是夠超越控件本身的最大寬度widthSpecSize,
若沒有超過履行
widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) {
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
超過控件的寬度履行
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine + verticalSpacing;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight + childUsedWidth;
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
最后調用 setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightUsed);這個方法去設置它的大小
3.在OnLayout方法里面,所做的工作就是去擺放每個孩子的位置 ,判斷需不需要換行,不需要更改left值,需要換行,更改top值
講授之前,我們先來了解1下1個基本知識
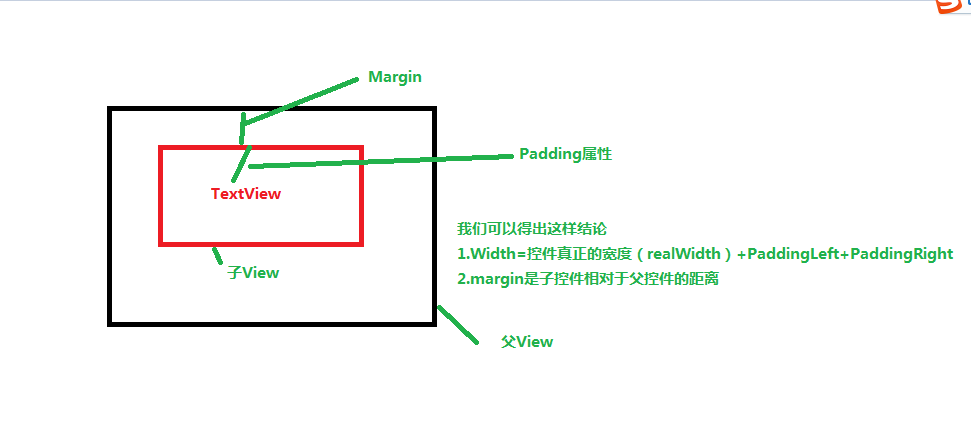
從這張圖片里面我們可以得出這樣結論
注意事項
為了支持控件本身的padding屬性,我們做了處理,主要代碼以下
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int heightUsed = paddingTop + paddingBottom;
----------
if (widthUsed + childUsedWidth < widthSpecSize) {
widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) {
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
}
為了支持子控件的margin屬性,我們一樣也做了處理
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childUsedWidth += leftMargin + rightMargin;
childUsedHeight += topMargin + bottomMargin;
即我們在計算孩子所占用的寬度和高度的時候加上margin屬性的高度,接著在計算需要孩子總共用的寬高度的時候加上每一個孩子的margin屬性的寬高度,這樣自然就支持了孩子的margin屬性了
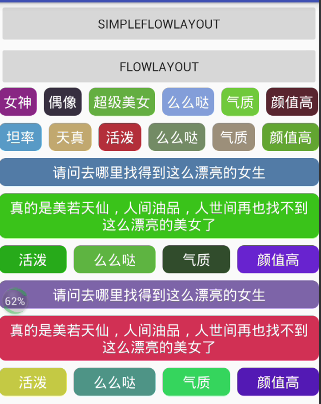
以下圖所見,在控件寬度良莠不齊的情況下,控件換行會留下1些剩余的寬度,作為想寫出魯棒性的代碼的我們會覺得別扭,因而我們相處了解決辦法。

解決方法見下面

/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu
* @author xujun
* @time 2016/6/26 22:54.
*/
public class PrefectFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
private int parentWidthSize;//父容器寬度
private int horizontalSpacing = 16;//水平間距
private int verticalSpacing = 16;//垂直間距
private Line currentLine;//當前行
private List<Line> mLines = new ArrayList<>();//所有行的集合
private int userWidth = 0;//當前行已使用寬度
/**
* 行對象
*/
private class Line {
private List<View> children;//1行里面所添加的子View集合
private int height;//當前行高度
private int lineWidth = 0;//當前行已使用寬度
public Line() {
children = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 添加1個子控件
*
* @param child
*/
private void addChild(View child) {
children.add(child);
if (child.getMeasuredHeight() > height) {
height = child.getMeasuredHeight();//當前行高度以子控件最大高度為準
}
lineWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth();//將每一個子控件寬度進行累加,記錄使用的寬度
}
/**
* 獲得行的高度
*
* @return
*/
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
/**
* 獲得子控件的數量
*
* @return
*/
public int getChildCount() {
return children.size();
}
/**
* 放置每行里面的子控件的位置
*
* @param l 距離最左側的距離
* @param t 距離最頂真個距離
*/
public void onLayout(int l, int t) {
//當前行使用的寬度,等于每一個子控件寬度之和+子控件之間的水平距離
lineWidth += horizontalSpacing * (children.size() - 1);
int surplusChild = 0;
int surplus = parentWidthSize - lineWidth;//剩余寬度
if (surplus > 0) {
//如果有剩余寬度,則將剩余寬度平分給每個子控件
surplusChild = (int) (surplus / children.size()+0.5);
}
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
View child = children.get(i);
child.getLayoutParams().width=child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild;
if (surplusChild>0){//如果長度改變了后,需要重新丈量,否則布局中的屬性大小還會是原來的大小
child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
,MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
child.layout(l, t, l + child.getMeasuredWidth(), t + child.getMeasuredHeight());
l += child.getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpacing;
}
}
}
// getMeasuredWidth() 控件實際的大小
// getWidth() 控件顯示的大小
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//將之前丈量的數據進行清空,以防復用時影響下次丈量
mLines.clear();
currentLine = null;
userWidth = 0;
//獲得父容器的寬度和模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
parentWidthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
//獲得父容器的高度和模式
int heigthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
int childWidthMode, childHeightMode;
//為了丈量每一個子控件,需要指定每一個子控件的丈量規則
//子控件設置為WRAP_CONTENT,具體丈量規則詳見,ViewGroup的getChildMeasureSpec()方法
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childWidthMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childWidthMode = widthMode;
}
if (heigthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childHeightMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childHeightMode = heigthMode;
}
//獲得到子控件高和寬的丈量規則
int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(parentWidthSize, childWidthMode);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize, childHeightMode);
currentLine = new Line();//創建第1行
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//丈量每個孩子
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();//獲得當前子控件的實際寬度
userWidth += childMeasuredWidth;//讓當前行使用寬度加上當前子控件寬度
if (userWidth <= parentWidthSize) {
//如果當前行使用寬度小于父控件的寬度,則加入該行
currentLine.addChild(child);
userWidth += horizontalSpacing;//當前行使用寬度加上子控件之間的水平距離
if (userWidth > parentWidthSize) {//如果當前行加上水平距離后超越父控件寬度,則換行
newLine();
}
} else {
if (currentLine.getChildCount() == 0) {//以防出現1個子控件寬度超過父控件的情況出現
currentLine.addChild(child);
}
newLine();
currentLine.addChild(child);//并將超越范圍確當前的子控件加入新的行中
userWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth()+horizontalSpacing;//并將使用寬度加上子控件的寬度;
}
}
if (!mLines.contains(currentLine)) {//加入最后1行,由于如果最后1行寬度不足父控件寬度時,就未換行
mLines.add(currentLine);
}
int totalHeight = 0;//總高度
for (Line line : mLines) {
totalHeight += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;//總高度等于每行的高度+垂直間距
}
setMeasuredDimension(parentWidthSize + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(),
resolveSize(totalHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(), heightMeasureSpec));//resolveSize(),將實際高度與父控件高度進行比較,選取最適合的
}
/**
* 換行
*/
private void newLine() {
mLines.add(currentLine);//記錄之前行
currentLine = new Line();//重新創建新的行
userWidth = 0;//將使用寬度初始化
}
/**
* 放置每一個子控件的位置
*
* @param changed
* @param l
* @param t
* @param r
* @param b
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
l += getPaddingLeft();
t += getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
Line line = mLines.get(i);
line.onLayout(l, t);//設置每行的位置,每行的子控件由其自己去分配
t += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;//距離最頂真個距離,即每行高度和垂直間距的累加
}
}
/**
* 獲得子控件的丈量規則
*
* @param mode 父控件的丈量規則
* @return 子控件設置為WRAP_CONTENT,具體丈量規則詳見,ViewGroup的getChildMeasureSpec()方法
*/
private int getMode(int mode) {
int childMode = 0;
if (mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childMode = mode;
}
return childMode;
}
}
對照圖1的實現思路,我們封裝了Line這個內部類,看到這個名字,相信大家都猜到是甚么意思了,其實就是1個Line實例對象代表1行,Line里面的List children用來寄存孩子
private List<View> children;//1行里面所添加的子View集合
Line里面還封裝了void onLayout(int l, int t)方法,即自己去造訪每一個孩子的位置,
實現剩余的寬度平均分配,主要體現在這幾行代碼
if (surplus > 0) {
//如果有剩余寬度,則將剩余寬度平分給每個子控件
surplusChild = (int) (surplus / children.size()+0.5);
}
-------
//重新分配每一個孩子的大小 child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
,MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
源碼下載地址:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/CustomViewDemo.git

上一篇 決策統計---指標六要素
下一篇 關于img ,你必須注意的