前言:不要嫌前進(jìn)的慢,只要1直在前進(jìn)就好。
相干文章:
1、《PopUpWindow使用詳解(1)――基本使用》
2、《PopUpWindow使用詳解(2)――進(jìn)階及答疑》
有同學(xué)講到想要知道PopUpWindow的知識(shí),這里就給大家講1講PopUpWindow的基本用法和原理吧。這段時(shí)間博客可能會(huì)更新比較慢,由于你懂的 !!-_- ,往左看公告,嘿嘿。
先看1下我們要做的效果:

這個(gè)效果很容易理解:當(dāng)點(diǎn)擊btn時(shí),在底部彈出PopupWindow,然后點(diǎn)擊各個(gè)item彈出對(duì)應(yīng)toast。
最關(guān)鍵的區(qū)分是AlertDialog不能指定顯示位置,只能默許顯示在屏幕最中間(固然也能夠通過設(shè)置WindowManager參數(shù)來改變位置)。而PopupWindow是可以指定顯示位置的,隨意哪一個(gè)位置都可以,更加靈活。
有關(guān)Dialog的相干知識(shí),大家可以參考我的系列博客:《詳解Dialog(1)――基礎(chǔ)元素構(gòu)建》
//方法1:
public PopupWindow (Context context)
//方法2:
public PopupWindow(View contentView)
//方法3:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height)
//方法4:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable)
重要注意:看這里有4個(gè)構(gòu)造函數(shù),但要生成1個(gè)PopupWindow最基本的3個(gè)條件是1定要設(shè)置的:View contentView,int width, int height ;少任意1個(gè)就不可能彈出來PopupWindow!!!!
所以,如果使用方法1來構(gòu)造PopupWindow,那完全的構(gòu)造代碼應(yīng)當(dāng)是這樣的:
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
PopupWindwo popWnd = PopupWindow (context);
popWnd.setContentView(contentView);
popWnd.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
popWnd.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
有關(guān)為何1定要設(shè)置width和height的緣由,我們后面會(huì)講,這里說1下為何樣強(qiáng)迫設(shè)置contentView;很簡單的緣由是由于PopupWindow沒有默許布局,它不會(huì)像AlertDialog那樣只setTitle,就可以彈出來1個(gè)框。PopupWindow是沒有默許布局的,它的布局只有通過我們自己設(shè)置才行。由于方法3中,含有了這3個(gè)必備條件,不用單獨(dú)設(shè)置contentview或width、height,所以構(gòu)造方法3是用的最多的1個(gè)構(gòu)造方法。
最后,方法4中的focusable變量不是必須的,有關(guān)它的方法和意義,我們會(huì)在下1篇中細(xì)講。
顯示函數(shù)主要使用下面3個(gè):
//相對(duì)某個(gè)控件的位置(正左下方),無偏移
showAsDropDown(View anchor):
//相對(duì)某個(gè)控件的位置,有偏移;xoff表示x軸的偏移,正值表示向左,負(fù)值表示向右;yoff表示相對(duì)y軸的偏移,正值是向下,負(fù)值是向上;
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff):
//相對(duì)父控件的位置(例如正中央Gravity.CENTER,下方Gravity.BOTTOM等),可以設(shè)置偏移或無偏移
showAtLocation(View parent, int gravity, int x, int y):
這里有兩種顯示方式:
1、顯示在某個(gè)指定控件的下方
showAsDropDown(View anchor):
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff);
2、指定父視圖,顯示在父控件的某個(gè)位置(Gravity.TOP,Gravity.RIGHT等)
showAtLocation(View parent, int gravity, int x, int y);
public void dismiss()
//另外幾個(gè)函數(shù),這里不講其意義,下篇細(xì)講
public void setFocusable(boolean focusable)
public void setTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background)
這幾個(gè)函數(shù)里,這篇只會(huì)用到dismiss(),用于不需要的時(shí)候,將窗體隱藏掉。
好了,空話不多說了,我們就做1個(gè)上面的例子來看1下。
在這個(gè)例子中,我們實(shí)現(xiàn)兩個(gè)功能,彈出popupWindow和Item點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
從效果圖中也能夠看到主布局只有1個(gè)button,甚么都沒有,所以它的布局代碼哪下:
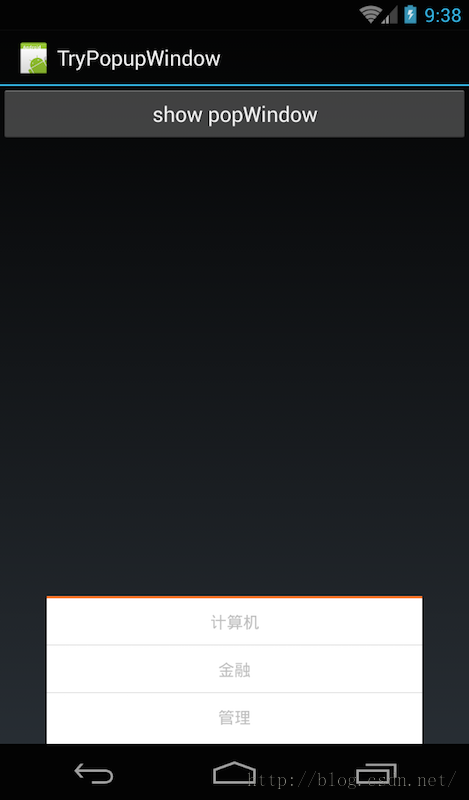
在概述中,我們提到了,必須為PopupWindow設(shè)置布局,從效果圖中,我也能夠看到它的布局有3個(gè)item,中間用橫線分開。所以這里布局使用Listview應(yīng)當(dāng)更適合,但為了減輕代碼難度,我們直接使用TextView和分隔線來代替,代碼以下:
先貼出來完全代碼,然后再逐漸講授:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener{
private PopupWindow mPopWindow;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPopupWindow();
}
});
}
private void showPopupWindow() {
//設(shè)置contentView
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, true);
mPopWindow.setContentView(contentView);
//設(shè)置各個(gè)控件的點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
TextView tv1 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
TextView tv2 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_financial);
TextView tv3 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_manage);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
//顯示PopupWindow
View rootview = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.main, null);
mPopWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int id = v.getId();
switch (id){
case R.id.pop_computer:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked computer",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_financial:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked financial",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_manage:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked manage",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
}
}
}
在OnCreate()中只做了1個(gè)操作,當(dāng)點(diǎn)擊Button時(shí),顯示窗體:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPopupWindow();
}
});
}
下面是有關(guān)窗體操作的代碼:
private void showPopupWindow() {
//設(shè)置contentView
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, true);
//設(shè)置各個(gè)控件的點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
TextView tv1 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
TextView tv2 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_financial);
TextView tv3 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_manage);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
//顯示PopupWindow
View rootview = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.main, null);
mPopWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0);
}
這里一樣分為3部份:
第1部份:設(shè)置ContentView
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, true);
利用LayoutInflater獲得R.layout.popuplayout對(duì)應(yīng)的View,然后利用我們上面所講的構(gòu)造函數(shù)3來生成mPopWindow;
這里 要注意1個(gè)問題:在這個(gè)構(gòu)造函數(shù)里,我們傳進(jìn)去了width和height全部都是WRAP_CONTENT;而在R.layout.popuplayou的根布局中,我們定義的width和height代碼是:layout_width="fill_parent",layout_height="wrap_content";原代碼以下:
………………
這里就有沖突了,那顯示出來的popupWindow是按哪一個(gè)來的呢?
從效果圖中來看,明顯PopupWindow寬度并沒有全屏,明顯是按代碼中的布局為準(zhǔn)。
這說明了:
**如果在代碼中重新設(shè)置了popupWindow的寬和高,那就以代碼中所設(shè)置為準(zhǔn)。**(至于緣由,下篇會(huì)講)
第2部份:設(shè)置各個(gè)控件的點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
TextView tv1 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
TextView tv2 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_financial);
TextView tv3 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_manage);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
這部份沒甚么好講了,設(shè)置PopupWindow中各個(gè)控件的點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng),但1定要注意的是,PopupWindow中各個(gè)控件的所在的布局是contentView,而不是在Activity中,如果大家直接使用
TextView tv1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
肯定會(huì)報(bào)錯(cuò),由于R.id.pop_computer這個(gè)ID值在當(dāng)前Activtiy的布局文件中是找不到的。只有在R.layout.popuplayout的布局文件中才會(huì)有!所以,這就是為何,要在findViewById(R.id.pop_computer)前指定contentView的緣由!!!在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中,很容易遇到像這類需要指定根布局的情況,大家需要注意。
有關(guān)響應(yīng),就沒甚么好講的了,由于我們在類頂部派生了View.OnClickListener,所以在OnClick函數(shù)中,直接處理便可,代碼以下:(在點(diǎn)擊不同的Item時(shí),1邊彈出不同的toast,1邊將PopupWindow隱藏掉)
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int id = v.getId();
switch (id){
case R.id.pop_computer:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked computer",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_financial:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked financial",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_manage:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked manage",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
}
}
第3部份:showAtLocation顯示窗體
View rootview = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.main, null);
mPopWindow.showAtLocation(rootview, Gravity.BOTTOM, 0, 0);
showAtLocation的顯示就將PopupWindow的實(shí)例放在1個(gè)父容器中,然后指定顯示在父容器中的位置。
由于,我們要將mPopWindow放在全部屏幕的最低部,所以我們將R.layout.main做為它的父容器。將其顯示在BOTTOM的位置。
到這里,有關(guān)PopupWindow的顯示及其中控件響應(yīng)基本都講完了,下面,我們就講講showAsDropDown顯示窗體的用法。
源碼在文章底部給出
大家先看下面這個(gè)效果圖:
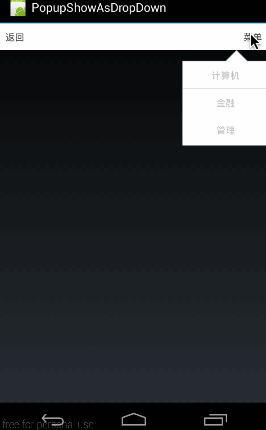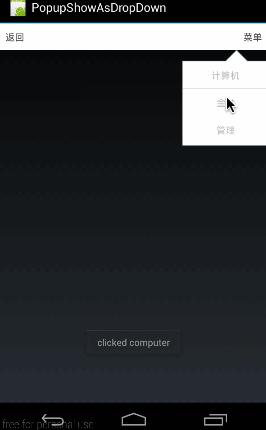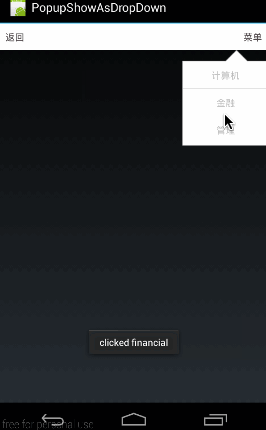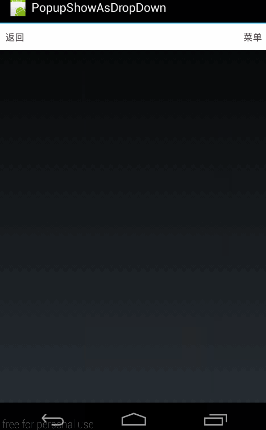
這個(gè)效果圖演示的是,在點(diǎn)擊標(biāo)題欄右方的“菜單”按鈕時(shí),在其下方顯示1個(gè)自定義的菜單列表。
這段代碼的布局很簡單,就是生成1個(gè)標(biāo)題欄,上面有兩個(gè)按鈕,“返回”和“菜單”
這部份布局也不難,只得利用純代碼硬生成1個(gè)列表的布局。在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中,大家應(yīng)當(dāng)使用listview來動(dòng)態(tài)生成列表,這樣生成的popupWindow就是可以復(fù)用的了。有關(guān)布局就不再多講,跟上面的布局基本1樣,只是換了背景。
一樣是先貼出來完全代碼,然后再細(xì)講。
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener{
private PopupWindow mPopWindow;
private TextView mMenuTv;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mMenuTv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.menu);
mMenuTv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPopupWindow();
}
});
}
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
TextView tv1 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
TextView tv2 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_financial);
TextView tv3 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_manage);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int id = v.getId();
switch (id){
case R.id.pop_computer:{
Toast.makeText(this, "clicked computer", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_financial:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked financial",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
case R.id.pop_manage:{
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked manage",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mPopWindow.dismiss();
}
break;
}
}
}
這段代碼的意義就是點(diǎn)擊menu彈出popupwindow,然后對(duì)各個(gè)item進(jìn)行響應(yīng),我們主要講講showPopupWindow() 這部份,對(duì)item響應(yīng)的部份與上個(gè)示例都1樣,就不再細(xì)講。
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
TextView tv1 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_computer);
TextView tv2 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_financial);
TextView tv3 = (TextView)contentView.findViewById(R.id.pop_manage);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
這里首先注意的1個(gè)地方,在這個(gè)示例中,我們是使用的構(gòu)造方法2來生成的PopupWindow實(shí)例的,一樣,再強(qiáng)調(diào)1遍:contentView,Width,Height這3個(gè)元素是必須設(shè)置的,缺1不可!至于為何要顯式設(shè)置Width,Height,我們下篇會(huì)講到。
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
然后就是使用showAsDropDown()顯示PopupWindow:
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
大家也現(xiàn)樣可使用showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff):來添加相對(duì)x軸和y軸的位移量。具體用法就不再細(xì)講,沒甚么難度,大家試1試便可。
好了,這部份示例也講完了,下面我們就在這個(gè)示例上升級(jí)1個(gè)功能:講講怎樣在彈出PopupWindow的同時(shí)利用陰影把背景全部給遮罩起來。
源碼在文章底部給出
這部份的效果圖是下面這樣的:

從效果圖中可以看出,這部份是上1個(gè)示例的升級(jí)版,就是在點(diǎn)出PopupWindow的同時(shí),把背景用半透明黑色遮罩住,像彈出AlertDialog1樣的效果。下面就來看看這個(gè)效果是怎樣實(shí)現(xiàn)的吧。
其實(shí)原理很簡單,使PopupWindow的界面充滿全屏,而實(shí)際的列表菜單只是其中的1個(gè)子布局便可,所以此時(shí)的PopupWindow的布局代碼以下:
可見在列表項(xiàng)外面又包了1層RelativeLayout,將列表的根布局LinearLayout靠父窗口右側(cè)顯示便可。給RelativeLayout添加了半透明背景android:background="#66000000"
這樣要非常注意的是,根布局RelativeLayout設(shè)置的android:layout_width和android:layout_height是無意義的,由于我們會(huì)通過代碼重新設(shè)置:
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
………………//設(shè)置各控件點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
在這里,我們通過代碼將PopupWindow的width和height設(shè)置為LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT。那大家可能會(huì)有疑問:為何我在xml中布局中明明寫好了根布局RelativeLayout的寬和高,為何非要我們在代碼中重新設(shè)置呢?不設(shè)置還顯示不出來…………
下篇,我們將會(huì)解答這個(gè)問題。
好啦,這個(gè)示例關(guān)鍵部份講完了,其它的大家就看源碼吧。
源碼在文章底部給出
先看看效果:

為PopupWindow添加動(dòng)畫其實(shí)不難,只需要使用1個(gè)函數(shù)便可:
//設(shè)置動(dòng)畫所對(duì)應(yīng)的style
mPopWindow.setAnimationStyle(R.style.contextMenuAnim);
下面就來看看具體是如何添加動(dòng)畫的
這段代碼的意義就是從底部進(jìn)入,即從Y軸100%的位置移動(dòng)到0的位置。有關(guān)動(dòng)畫的知識(shí),大家可以參考《Animation 動(dòng)畫詳解(1)――alpha、scale、translate、rotate、set的xml屬性及用法》 這個(gè)系列文章。
效果是從上向下移動(dòng)。
android:windowEnterAnimation設(shè)置進(jìn)場動(dòng)畫,android:windowExitAnimation設(shè)置出場動(dòng)畫。
使用時(shí)非常簡單,直接將對(duì)應(yīng)的style通過setAnimationStyle設(shè)置進(jìn)PopupWindow實(shí)例便可,代碼以下,難度不大,不再細(xì)講。
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
………………//設(shè)置各子項(xiàng)點(diǎn)擊響應(yīng)
mPopWindow.setAnimationStyle(R.style.contextMenuAnim);
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
到這里,這個(gè)示例的代碼就講完了。源碼在文章底部1起給出。這篇講述了有關(guān)PopupWindow的基本使用方法,下篇將針對(duì)還未講述的幾個(gè)函數(shù),和問題點(diǎn)結(jié)合源碼深入剖析。
源碼內(nèi)容:
1、《PopshowAtLocation》:第2部份:簡單示例(showAtLocation顯示窗體)對(duì)應(yīng)源碼
2、《PopupShowAsDropDown》:第3部份:另外一示例(showAsDropDown顯示窗體) 對(duì)應(yīng)源碼
3、《PopDropDownBg》:第4部份:提高:為菜單添加陰影 對(duì)應(yīng)源碼
4、《PopupAnim》:第5部份:為PopupWindow添加動(dòng)畫 對(duì)應(yīng)源碼
