每一個Java程序員應當?shù)奶匦?/p>
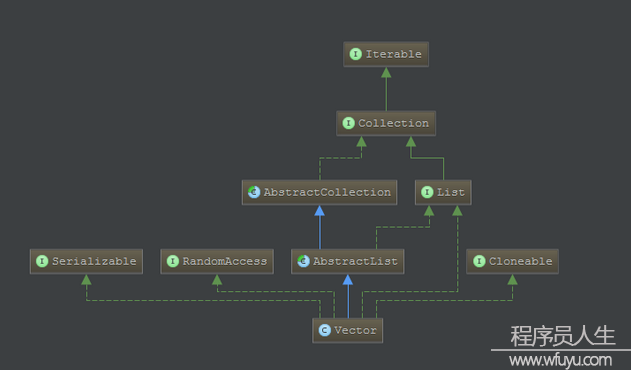
grow or shrink)accessed using an integer index)類圖
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
/*
vector 通過capacity(容量)和capacityIncrement(增量)兩個屬性來最化管理存儲, capacity 1般都比 size 大。
當知道需要插入大量元素時,可以提早分配給vector較大空間,減少分配內(nèi)存次數(shù), 從而減少沒必要要的開消。
此類的iterator和listIterator方法返回的迭代器是快速失敗的:如果該向量在任什么時候間從結構上修改創(chuàng)建迭代器后,
以任何方式,除通過迭代器本身的remove或add方法,迭代器都將拋出ConcurrentModificationException。
因此,在并發(fā)的修改,迭代器很快就會完全失敗,而不是在將來不肯定的時間任意冒險,不肯定性的行動。
通過elements方法返回的Enumeration不是快速失敗的。
注意,迭代器的快速失敗行動不能得到保證,由于它是,1般來講,
不可能作出任何硬性保證不同步并發(fā)修改的存在。快速失敗迭代器拋出ConcurrentModificationException盡最大努力的基礎上。
因此,這將是毛病的編寫1個程序,依賴于此異常為它的正確性:
迭代器的快速失敗行動應當僅用于檢測bug。
從Java 2平臺v1.2,這個類是改進來實現(xiàn)List接口,使它成為Java Collections Framework的成員。
不同的是新的集合實現(xiàn)不同,Vector是同步的。
如果不需要線程安全履行,建議代替矢量的使用的ArrayList。
*/
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 寄存數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)組
protected Object[] elementData;
// 實際元素個數(shù)
protected int elementCount;
// 容量增量,每次擴容增加的大小,如果 capacityIncrement小雨或等于0,那末容量會每次翻倍double的增長
protected int capacityIncrement;
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
// 數(shù)組的初始化,增量的初始化,容量小于0會報異常
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
// 指定容量,并且增量為0,每次擴容方法為翻倍
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
//默許構造方法,默許容量大小為10
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
// 根據(jù)指定集合創(chuàng)建vector
// 另外vector的順序由集合Collection的iterator遍歷的順序來保證
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray(); // 根據(jù)集合生成數(shù)組,數(shù)組是reallocate的,不存在refer關系
elementCount = elementData.length;
//下面1句話簡單理解就是 toArray()返回的其實不1定是Object[]數(shù)組(實際類型)
// 具體請看 我的博客文章 http://blog.csdn.net/huzhigenlaohu/article/details/51702737
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
/**
* anArray 為空會報空指針異常 , anArray的長度不能容納elementData所有元素匯會報索引越界異常
* 另外 c.toArray not return Object[]時候 報 ArrayStoreException
* 請看 http://blog.csdn.net/huzhigenlaohu/article/details/51702737
*/
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
// 去掉Vector 數(shù)組后面未存入數(shù)據(jù)的部份,使得Capacity(length) = elementCount
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
//這個 字段含義為 vector 結構(1般指的是大小)被修改的次數(shù)
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
//擴容函數(shù)(對外暴露的函數(shù),實現(xiàn)看grow)
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//這個才是看的重點,上面兩個函數(shù)可以疏忽掉。。。額,說錯了,不是疏忽掉而是可以不看
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 如果增量大于0那末是的容量+Increment,如果小于等于0,那末容量翻倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
// 如果根據(jù)擴容方法后容量還是小于minCapacity,那末設置擴容后大小為minCapacity
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//溢出,大于最大允許的容量
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//根據(jù)容量重新reallocate內(nèi)存,得到1個新數(shù)組
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// 容量超過最大值處理方式
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
// 設置vector 的size大小,注意其實不是length,當設置的newsize大于當前的size那末斟酌是不是要擴容,如果小于,那末把過剩的部份全部設置為null
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
//容量
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
//元素個數(shù)
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
//實際存儲的元素是不是為空
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
//根據(jù)索引生成 對應元素的枚舉 ,索引為0 為枚舉第1個元素,索引為1為枚舉第2個元素,and so on
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
//可以看到此方法會拋出異常,在調(diào)用的時候務必先調(diào)用hasMoreElements進行判斷
public E nextElement() {
//提供vector對象鎖,保持同步
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return elementData(count++);
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
//辨別是不是存在對象 o
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
//返回第1個出現(xiàn)o的位置索引
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
//主要是判斷o是不是為空,其他都是順序查找,很簡單O(n)
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//從數(shù)組后端開始查找起,出現(xiàn)的第1個元素
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
//主要是判斷o是不是為空,其他都是順序查找,很簡單O(n)
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//方法同等于List接口的get(i)方法說
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(0);
}
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(elementCount - 1);
}
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
//刪除從數(shù)組左側起第1個與obj相等的元素
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//刪除所有元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// Let gc do its work
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null; //gc垃圾回收
elementCount = 0;
}
// clone克隆Vector,重新生成的數(shù)組與原來的數(shù)組屬于不同援用,重新分配內(nèi)存
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {//泛型指定生成的數(shù)組的類型
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount);
if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null;
return a;
}
//沒同步,也沒判斷會不會拋出異常,為何會存在呢?由于這個方法外部不能調(diào)用,它由其他內(nèi)部(public)同步方法調(diào)用,保證線程安全
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
//返回的是舊值
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
//返回被移除的對象
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
//清空
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
}
// 批量操作,判斷vector中是不是包括集合
// 特別注意:判斷集合集合中每一個元素是不是都存在vector中,并沒有順序可言,單獨判斷,復雜度為O(m*n)
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
// 父類方法AbstractCollection
/*
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
for (Object e : c)
if (!contains(e))
return false;
return true;
}
*/
}
//集合到vector中,會拋出空指針異常
//特別注意:當正在進行此操作的時候,集合C又被另外1個線程修改,那末得到的vector是不肯定的
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 刪除指定集合中切存在于vector中的元素
// 遍歷vector中每一個元素,判斷是不是存在于collection中,存在則刪除,復雜度為O(M*n)
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
}
// 與前面1個函數(shù)功能相反,保存存在于Collection中的vector的元素
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
}
//指定索引,插入集合
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
int numMoved = elementCount - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 順序、值、大小都要相等,使用父類AbstractList方法實現(xiàn),順序由listIterator()保證
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
}
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
//AbstractCollection方法
/*
public String toString() {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
*/
// 根據(jù)指定索引,返回子集合
//特別注意: 返回的子集合還是依賴于此vector的,其實不是重新分配內(nèi)存的
//對子集合的1切操作將會影響vector的變化,比如對子集合的排序(這個利用的非常廣)、清空子集合等都會影響vector元素變化,但是與此同時也要斟酌到多線程的不肯定性
//eg:list.subList(from, to).clear();清空
//由于使用了Collections.synchronizedList進行同步處理(對象鎖為當前vector對象),因此對vector的操作和對子集合的操作是同步處理的
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex),
this);
}
//刪除指定范圍子集合
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// Let gc do its work
int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (elementCount != newElementCount)
elementData[--elementCount] = null;
}
//序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
final java.io.ObjectOutputStream.PutField fields = s.putFields();
final Object[] data;
synchronized (this) {
fields.put("capacityIncrement", capacityIncrement);
fields.put("elementCount", elementCount);
data = elementData.clone();
}
fields.put("elementData", data);
s.writeFields();
}
// 返回指定游標的列表迭代器,此迭代器ListIterator可以向前向后迭代,比普通iterator()方法強大Itr,推薦使用
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
//同上1個方法,默許游標位置為起始位置0
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
//返回1個迭代器
public synchronized Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
//迭代器默許實現(xiàn),會出現(xiàn)fail-fast機制
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; ⑴ if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
// Racy but within spec, since modifications are checked
// within or after synchronization in next/previous
return cursor != elementCount;
}
public E next() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();//檢查在迭代期間,檢查vector是不是存在結構修改
int i = cursor;
if (i >= elementCount)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i + 1;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.remove(lastRet);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
synchronized (Vector.this) {
final int size = elementCount;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) Vector.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
action.accept(elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//列表迭代器,可以向前向后遍歷
final class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public E previous() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.set(lastRet, e);
}
}
public void add(E e) {
int i = cursor;
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.add(i, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
}
}
//jdk1.8 新加入的方法,遍歷vector中每一個元素,并利用于action行動,支持lambda表達式
@Override
public synchronized void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int elementCount = this.elementCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < elementCount; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//支持lambda表達式,判斷是不是復合某種條件,然后做其他操作
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// figure out which elements are to be removed
// any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage
// will leave the collection unmodified
int removeCount = 0;
final int size = elementCount;
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);//位集合,記錄符合條件的元素的索引
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
if (filter.test(element)) {
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
//刪除符合條件的元素,左移
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
elementCount = newSize;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}
//支持lambda表達式,對全部元素進行替換操作
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = elementCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
// Arrays.sort 排序
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, elementCount, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}, and {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
* Overriding implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new VectorSpliterator<>(this, null, 0, -1, 0);
}
/** Similar to ArrayList Spliterator */
static final class VectorSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
private final Vector<E> list;
private Object[] array;
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // ⑴ until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */
VectorSpliterator(Vector<E> list, Object[] array, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.array = array;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
synchronized(list) {
array = list.elementData;
expectedModCount = list.modCount;
hi = fence = list.elementCount;
}
}
return hi;
}
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null :
new VectorSpliterator<E>(list, array, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (getFence() > (i = index)) {
index = i + 1;
action.accept((E)array[i]);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
Vector<E> lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
synchronized(lst) {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
a = array = lst.elementData;
hi = fence = lst.elementCount;
}
}
else
a = array;
if (a != null && (i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
while (i < hi)
action.accept((E) a[i++]);
if (lst.modCount == expectedModCount)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
}
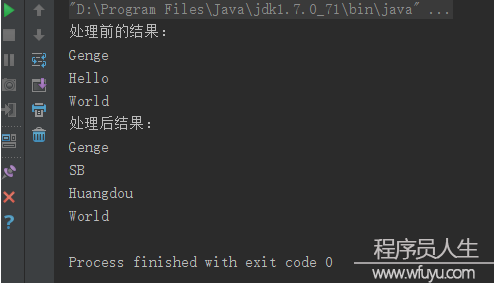
subList() 用法/**
* Created by Genge on 2016-06⑴9.
*/
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<String> vector = new Vector<String>();
vector.add("Genge");
vector.add("Hello");
vector.add("World");
System.out.println("處理前的結果:");
Iterator<String> iterator = vector.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
List<String> sublist = vector.subList(1, 2);
sublist.clear();
sublist.add("SB");
sublist.add("Huangdou");
System.out.println("處理后結果:");
Iterator<String> iter = vector.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}
}結果圖以下: