STL之容器map
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2015-09-09 08:37:48 閱讀次數:3228次
1.首先介紹map具有與set集合一樣的自動排序功能
插入方法之pair<>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
m.insert(pair<int,string>(2,"student_two"));
m.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"student_one"));
m.insert(pair<int,string>(3,"student_three"));
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
}
return 0;
//輸出
//1 student_one
// 2 student_two
// 3 student_three
// Press any key to continue
}
2.插入之value_type
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (2,"student_two"));
m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (1,"student_one"));
m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (3,"student_three"));
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
}
return 0;
//輸出
//1 student_one
// 2 student_two
// 3 student_three
// Press any key to continue
}
3.插入之數組
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
m[2] = "student_two";
m[1] = "student_one";
m[3] = "student_three";
// m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (2,"student_two"));
// m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (1,"student_one"));
// m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (3,"student_three"));
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
}
return 0;
//輸出
//1 student_one
// 2 student_two
// 3 student_three
// Press any key to continue
}
以上3種方法實際上是有區分的,第1種和第2種沒有區分,第3種的數組有區分。在map數據的插入上觸及到唯1性的概念,即當map中有這個關鍵字時,insert是插入不了重復的數據的,就像之前的set1樣,但是數組可以插入,但是會覆蓋掉之前對應的關鍵字的值,下面用
程序來講明
m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (1,"student_two"));
m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (1,"student_one"));
上面兩條語句履行后,map中的1這個關鍵字對應的值是student_two,第2條語句并未生效,所以我們需要知道第2條語句有沒有插入成功:
pair<map<int,string>::iterator,bool>insert_type;
insert_type = m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(1,"student_one"));
我們通過pair的第2個變量bool來判斷數據是不是插入成功,當插入成功后,insert_type.second應當是true,反之為false。
下面給出代碼來演示:
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
pair<map<int,string>::iterator,bool>insert_type;
insert_type = m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(1,"student_one"));
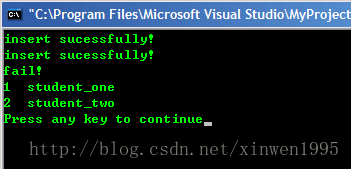
if(insert_type.second == true)
{
cout<<"insert sucessfully!"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"fail!"<<endl;
}
insert_type = m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(2,"student_two"));
if(insert_type.second == true)
{
cout<<"insert sucessfully!"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"fail!"<<endl;
}
insert_type = m.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(1,"student_three"));
if(insert_type.second == true)
{
cout<<"insert sucessfully!"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"fail!"<<endl;
}
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
}
return 0;
}
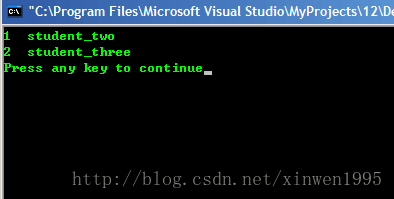
2.用數組重復插入
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
m[1] = "student_one";
m[1] = "student_two";
m[2] = "student_three";
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
}
return 0;
}
數據的查找
1.count函數查找 缺點:沒法返回所要查找的數據的位置
由于map中的數據都是1對1的映照關系,所以count的返回值只有2個,0,1。
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>m[1] = "student_one";
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>m[2] = "student_two";
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>m[3] = "student_three";
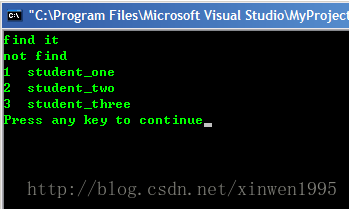
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>if(m.count(2)) cout<<"find it"<<endl;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>else
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>cout<<"not find"<<endl;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>if(m.count(4)) cout<<"find it"<<endl;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>else
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>cout<<"not find"<<endl;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>map<int,string>::iterator it;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>for (it = m.begin();it != m.end();it++)
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; //first與second分別指的是map<int,string>中的int和string
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>return 0;
}
第2種:用find。 優點:可以返回要查詢的數據的迭代位置
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> m; //必須有兩個類型
m[1] = "student_one";
m[2] = "student_two";
m[3] = "student_three";
map<int,string>::iterator it;
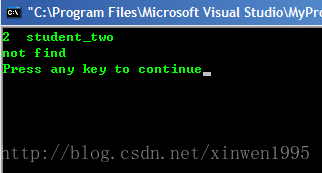
it = m.find(2);
if(it != m.end())
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl;
else
cout<<"not find"<<endl;
it = m.find(4);
if(it != m.end())
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl;
else
cout<<"not find"<<endl;
return 0;
}
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈





