Java基礎(chǔ)――集合(二)――迭代器、Map集合
來源:程序員人生 發(fā)布時間:2015-06-12 08:53:27 閱讀次數(shù):3611次
接上篇,《Java基礎(chǔ)――集合(1)――集合體系和Collection》
4.迭代器的使用
使用步驟:
1、通過集合對象獲得迭代器對象。
2、通過迭代器對象判斷。
3、通過迭代器對象獲得。
迭代器原理
由于多種集合的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)不同,所以存儲方式不同,所以,取出方式也不同。
這個時候,我們就把判斷和獲得功能定義在了1個接口中,將來,遍歷哪一種集合的時候,只要該集合內(nèi)部實現(xiàn)這個接口便可。
迭代器源碼
public interface Iterator
{
publicabstract boolean hasNext();
publicabstract Object next();
}
publicinterface Collection
{
publicabstract Iterator iterator();
}
publicinterface List extends Collection
{
...
}
publicclass ArrayList implements List
{
publicIterator iterator()
{
returnnew Itr();
}
privateclass Itr implements Iterator
{
publicboolean hasNext(){...}
publicObject next(){...}
}
}
Collection存儲字符串和自定義對象并通過迭代器遍歷
1、存儲字符串
Collectionc = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
Iteratorit = c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Strings = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
2、存儲自定義對象(Student類的代碼省略)
Collection c=newArrayList();
Student s1=newStudent("林青霞",26);
c.add("s1");
Iteratorit=c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
Strings=(String)it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
ListIterator迭代器是Iterator的子接口
所以List的遍歷方式共有3種
1、Iterator迭代器
2、ListIterator迭代器
3、普通for+get()
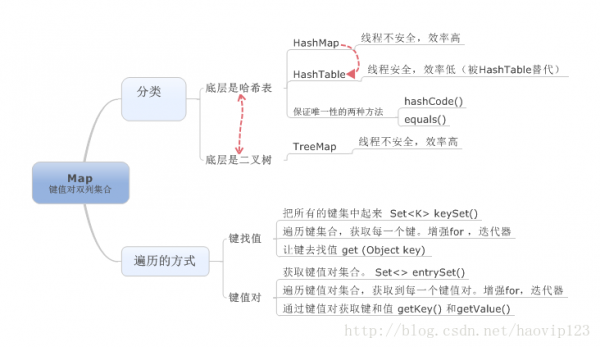
5.Map
map是1個鍵值對情勢的集合。它的元素都是有鍵和值組成。Map的鍵(key)是唯1的,值(value)可以重復。
Map的功能:
A:添加功能
V put(K key ,V value) :當key在集合中不存在是,添加元素;當key存在時替換元素
B:判斷功能
booleancontainsKey (Object key) :判斷指定的鍵是不是在集合中存在
BooleancontainsValue(Object value):判斷指定的值是不是在集合中存在
BooleanisEmpty() :判斷集合是不是為空
C:刪除功能
Voidclear():清除所有鍵值對數(shù)據(jù)
D:獲得功能
Objectget (Object key) :根據(jù)鍵獲得值
Set<K> keyset(): 所有鍵的集合
Collection<V>values() :所有值的集合
E:長度功能
Intsize()
Map包括HashMap、HashTable和TreeMap。其中,HashTable已基本被HashMap取代,這里不做討論。
Map遍歷的兩種方式:(導圖上面已有,這里直接上代碼了)
鍵找值:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer>map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("2陽",23);
map.put("2崢",24);
map.put("2光",25);
Set<String> keys=map.keySet(); //把鍵其中起來,存入到set集合中.
for(Stringkey:keys){ //遍歷鍵集合,獲得每個鍵。增強for
Integervalue=map.get(key); //讓鍵去找值 get(Object key)
System.out.println(key+"***"+value);
}
}
鍵值對:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer>map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("2陽",23);
map.put("2崢",24);
map.put("2光",25);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set=map.entrySet(); //獲得鍵值對集合。Set<> entrySet()
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> me:set){ //遍歷鍵值對集合,獲得到每個鍵值對。增強for,迭代器
Stringkey=me.getKey(); //通過鍵值對獲得鍵getKey()
Integervalue=me.getValue(); //通過鍵值對獲得值getValue()
System.out.println(key+"***"+value);
}
}
未完待續(xù),下篇為泛型+增強for+工具類
生活不易,碼農(nóng)辛苦
如果您覺得本網(wǎng)站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈


