遞歸函數,也就是不斷的調用本身的函數,使用遞歸能夠比較方便的解決1些比較難使用循環解決的問題。就在這個例子中,求1個數組a[]的前n項和,也就是求a[n⑴]+a[n⑵]+…+a[0],那末如果1個函數sum是用來求數組前n項和的,sum定義為sum(int a[],int n),則使用遞歸的方式就是
a[n⑴]+sum(a,n⑴)。
使用代碼來表述可能更好1些:
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int test[],int n);
/**
* @brief main 使用遞歸求1個數組的前n個元素的和
* 假定數組為a[];則求其前n的元素的和也就是求
* a[n⑴]+a[n⑵]+...a[0]
* @return
*/
int main(void)
{
int n;
printf("Please input the number of an array:
");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Please enter the element of the array:
");
int test[n];
int i;
for(i = 0;i < n;i++)
scanf("%d",&test[i]);
int count = sum(test,n);
printf("The sum of the array is : %d.
",count);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief sum 實現前n個元素的和
* @param test 要求和的數組
* @param n 所要求的前n個元素
* @return 返回前n個元素的和
*/
int sum(int test[],int n){
if(n <= 0)
return 0;
return test[n-1]+sum(test,n-1);
}
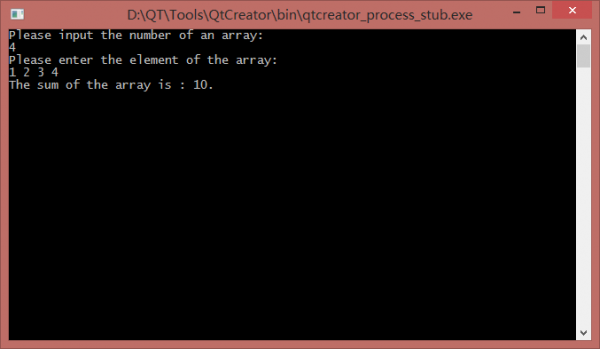
下面是我的程序的輸出,這個程序比較簡單。