在上1篇教程中,我們在Cloud9中跑通了全部演示代碼,下面我們將從零建立1個新的Rails利用。
在我們寫代碼之前,我們先看看Rails框架的結(jié)構(gòu):
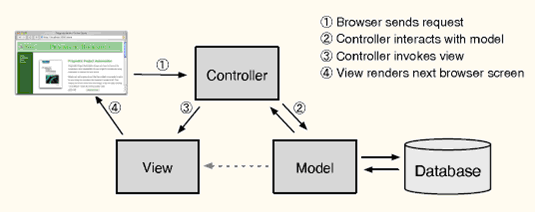
Rails框架最主要的特點是遵守MVC的設(shè)計模式(M:model,V:view,C:controller),也就是控制器-視圖-模型模式。Rails框架將代碼邏輯實現(xiàn)在控制器(controller)中,將與數(shù)據(jù)庫的操作實現(xiàn)在模型(model)中,將與用戶交互的網(wǎng)頁元素(HTML、JS、CSS)實現(xiàn)在視圖中。通過分離這3大部份的功能,Rails能很好的保持1個清晰的架構(gòu)。
在上圖的第1步中還遺留了1個routing(路由)的進程。
我們利用1個完全的進程來論述上述進程,假定用戶在閱讀器中輸入這個網(wǎng)址并提交:
http://whatever.com/users/index,當(dāng)服務(wù)器(whatever.com)接收到這個要求,將會把要求交給控制器users_controller中的方法index處理,為何服務(wù)器知道如何把這個要求交給這個控制器和這個控制器下的index方法呢?
是由于Rails有個routes.rb文件,里面配置了要求的映照關(guān)系,因此Rails在每次處理用戶要求時,都會去這個文件里查找映照關(guān)系,再根據(jù)映照的結(jié)果交給適合的控制器和控制下的方法,在這里users叫做資源,index叫做處理資源的方法。這個進程就叫做路由。Rails在表示資源的時候利用了RESTful的理念。
1.在C9登錄后的界面中點擊創(chuàng)建新的項目,以下:
以上的配置會默許創(chuàng)建新的Rails App
2.C9為我們生成好了1個Rails框架的文件模板,首先我們看1下文件樹:
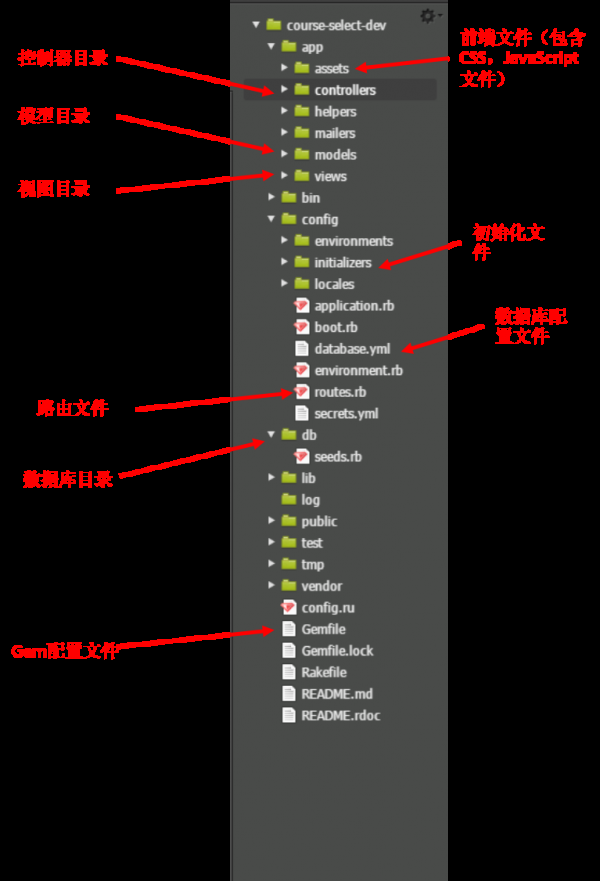
bundle install 這個指令就是安裝所有在這個列表下的外部庫。3.點擊Run Project,我們就能夠運行這個新的Rails App
Rails開發(fā)流程是先創(chuàng)建模型,再創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)控制器,配置相干路由,然后在控制器下創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)方法,最后對應(yīng)每一個方法創(chuàng)建視圖。
模型是甚么,模型代表了1個底層數(shù)據(jù)表的類,封裝了操作這個數(shù)據(jù)表的各種方法。
1.由因而學(xué)生選課系統(tǒng),我們肯定需要1個數(shù)據(jù)表來貯存用戶的信息,需要1張數(shù)據(jù)表來貯存課程的信息,那末我們運行以下指令創(chuàng)建用戶模型和課程模型:
pengzhaoqing:~/workspace $ rails generate model course
Running via Spring preloader in process 3251
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/20160920163906_create_courses.rb
create app/models/course.rb
invoke test_unit
create test/models/course_test.rb
create test/fixtures/courses.yml
pengzhaoqing:~/workspace $ rails generate model user
Running via Spring preloader in process 3262
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/20160920163927_create_users.rb
create app/models/user.rb
invoke test_unit
create test/models/user_test.rb
create test/fixtures/users.ymlrails generate model course 指令,Rails就幫我們創(chuàng)建了 db/migrate/20160920163906_create_courses.rb、app/models/course.rb、等test文件,省去了開發(fā)人員自己創(chuàng)建文件的麻煩。2.現(xiàn)在我們到打開db/migrate/20160920163906_create_courses.rb文件,填入:
class CreateCourses < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :courses do |t|
t.string :name
t.string :course_code
t.string :course_type
t.string :teaching_type
t.string :exam_type
t.string :credit
t.integer :limit_num
t.integer :student_num, default: 0
t.string :class_room
t.string :course_time
t.string :course_week
t.belongs_to :teacher
t.timestamps null: false
end
end
endcourses這個表中的字段和字段類型,Rails將會依照這個文件中描寫的進行建立數(shù)據(jù)表。這里我們并沒有配置database.yml文件,Rails默許的就是內(nèi)置的Sqlite3數(shù)據(jù)庫,可以自己去看看那個文件里面的adapter是否是指定的sqlite33.相同地,我們打開db/migrate/20160920163927_create_users.rb,填入:
class CreateUsers < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :users do |t|
t.string :name
t.string :email
t.string :num
t.string :major
t.string :department
t.string :password_digest
t.string :remember_digest
t.boolean :admin, default: false
t.boolean :teacher,default: false
t.timestamps null: false
end
add_index :users, :email, unique: true
end
endadmin 和 teacher add_index :users, :email, unique: true email字段建立索引,為以后能快速地根據(jù)用戶郵箱檢索到某個用戶。4.在選課系統(tǒng)中,1個學(xué)生有多門課,1門課可以被多名學(xué)生選擇,因此學(xué)生和課程就是多對多的關(guān)系,而且,每一個學(xué)生的每門課都有1個成績。這里觸及了3個數(shù)據(jù)實體,1個是學(xué)生,1個是課程,1個是成績。所以,我們還需要創(chuàng)建1個關(guān)于成績的數(shù)據(jù)表,里面貯存著學(xué)生表的主鍵(user_id)和課程表的主鍵(course_id)和對應(yīng)的成績。
下面,我們運行rails generate model grade 建立成績模型:
pengzhaoqing:~/workspace $ rails generate model grade
Running via Spring preloader in process 1144
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/20160921051153_create_grades.rb
create app/models/grade.rb
invoke test_unit
create test/models/grade_test.rb
create test/fixtures/grades.yml進入db/migrate/20160921051153_create_grades.rb,建立相應(yīng)的字段:
class CreateGrades < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :grades do |t|
t.belongs_to :course, index: true
t.belongs_to :user, index: true
t.integer :grade
t.timestamps null: false
end
end
end這里的t.belongs_to: :course 就等于 t.integer :course_id,記錄了課程表中課程的id。如此表示的意圖在于更加清晰地表達模型之間的從屬關(guān)系:
1個課程具有多個成績,1個成績只屬于1個課程;1個學(xué)生具有多個成績,1個成績只屬于1個學(xué)生;學(xué)生和課程兩個屬性能唯1肯定成績
5.分析到這里,我們是不會遺忘了甚么,對,就是這個:1個老師上多門課,每門屬于1個老師。這里老師和課程是也是1對多的關(guān)系(為了簡化,就不再設(shè)計為多對多的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系了),回顧我們在課程模型的數(shù)據(jù)遷移文件db/migrate/20160920163906_create_courses.rb 中寫的1句代碼t.belongs_to :teacher,就已將用戶(老師)的id作為外鍵貯存在課程模型的數(shù)據(jù)表中,目的就是要實現(xiàn)用戶(老師)與課程模型的1對多關(guān)系,即在課程模型的數(shù)據(jù)表中查找某個用戶(老師)的id,就可以將取出與這個id相干的所有課程的數(shù)據(jù)。
6.我們直接畫出ER圖來看各個模型之間的關(guān)系:
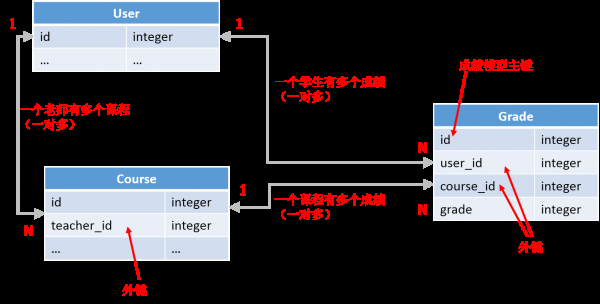
需要注意的是,上圖中,用戶模型和課程模型通過成績模型關(guān)聯(lián)起來了(由于可以根據(jù)user_id查詢所有相干的course_id,而且根據(jù)course_id也能夠反過來查詢所有的user_id),也就實現(xiàn)了用戶模型和課程模型多對多的關(guān)系。
7.到這里,我們已完成了模型數(shù)據(jù)字段的建立進程,下面我們要把這些字段之間的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系告知Rails框架,然后Rails就可以自動幫我們組織各模型之間的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系。首先打開app/models/course.rb,填入:
class Course < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many :grades
has_many :users, through: :grades
belongs_to :teacher, class_name: "User"
validates :name, :course_type, :course_time, :course_week,
:class_room, :credit, :teaching_type, :exam_type, presence: true, length: {maximum: 50}
endhas_many方法描寫與其他模型的1對多的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系。through 參數(shù)描寫了:此1對多關(guān)系是通過成績模型才關(guān)聯(lián)到用戶模型的。belongs_to 方法描寫了與其他模型的多對1的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系,class_name 指定了用戶模型的類名,這樣Rails才能正確找到關(guān)聯(lián)的用戶模型。validates 方法指定了對模型下的字段的驗證,這里1共驗證了:name, :course_type, :course_time, :course_week, :class_room, :credit, :teaching_type, :exam_type 8個字段,驗證要求是 presence: true, length: {maximum: 50},表示各個字段要存在(不為空)而且最大長度不能超過50個字符。驗證會在每次保存課程數(shù)據(jù)的時候履行8.下1步,打開app/models/grade.rb,填入:
class Grade < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :course
belongs_to :user
end9.接著打開app/models/user.rb,填入:
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
before_save :downcase_email
attr_accessor :remember_token
validates :name, presence: true, length: {maximum: 50}
validates :password, presence: true, length: {minimum: 6}, allow_nil: true
has_many :grades
has_many :courses, through: :grades
has_many :teaching_courses, class_name: "Course", foreign_key: :teacher_id
VALID_EMAIL_REGEX = /\A[\w+\-.]+@[a-z\d\-.]+\.[a-z]+\z/i
validates :email, presence: true, length: {maximum: 255},
format: {with: VALID_EMAIL_REGEX},
uniqueness: {case_sensitive: false}
#1. The ability to save a securely hashed password_digest attribute to the database
#2. A pair of virtual attributes (password and password_confirmation), including presence validations upon object creation and a validation requiring that they match
#3. An authenticate method that returns the user when the password is correct (and false otherwise)
has_secure_password
# has_secure_password automatically adds an authenticate method to the corresponding model objects.
# This method determines if a given password is valid for a particular user by computing its digest and comparing the result to password_digest in the database.
# Returns the hash digest of the given string.
def User.digest(string)
cost = ActiveModel::SecurePassword.min_cost ? BCrypt::Engine::MIN_COST :
BCrypt::Engine.cost
BCrypt::Password.create(string, cost: cost)
end
def User.new_token
SecureRandom.urlsafe_base64
end
def user_remember
self.remember_token = User.new_token
update_attribute(:remember_digest, User.digest(remember_token))
end
def user_forget
update_attribute(:remember_digest, nil)
end
# Returns true if the given token matches the digest.
def user_authenticated?(attribute, token)
digest = self.send("#{attribute}_digest")
return false if digest.nil?
BCrypt::Password.new(digest).is_password?(token)
end
private
def downcase_email
self.email = email.downcase
end
endhas_many :courses, through: :grades has_many :teaching_courses, class_name: "Course", foreign_key: :teacher_id has_many :courses, through: :grades,Rails在解釋代碼的時候就會默許去找有無叫course.rb(復(fù)數(shù)變單數(shù))的文件,而且還會去這個course模型下找有無叫user_id的外鍵字段。但是,根據(jù)第2句代碼中的teaching_courses,Rails沒法正確找到course.rb文件(這就不是僅僅是復(fù)數(shù)變單數(shù)那末簡答了!),所以我們需要手動指定它去找1個叫做Course類的模型和關(guān)聯(lián)模型下的外鍵teacher_iddigest,new_token,user_remember,user_forget, user_authenticated?, downcase_email都是在后面用戶登錄功能需要用到的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)功能,詳細內(nèi)容請進傳送門9.所有的模型和模型的數(shù)據(jù)遷移文件我們都建立好了,下面運行數(shù)據(jù)遷移rake db:migrate建立數(shù)據(jù)表,成功會看到以下信息:
pengzhaoqing:~/workspace $ rake db:migrate
== 20160920163906 CreateCourses: migrating ====================================
-- create_table(:courses)
-> 0.0079s
== 20160920163906 CreateCourses: migrated (0.0080s) ===========================
== 20160920163927 CreateUsers: migrating ======================================
-- create_table(:users)
-> 0.0014s
-- add_index(:users, :email, {:unique=>true})
-> 0.0011s
== 20160920163927 CreateUsers: migrated (0.0028s) =============================
== 20160921051153 CreateGrades: migrating =====================================
-- create_table(:grades)
-> 0.0039s
== 20160921051153 CreateGrades: migrated (0.0042s) ============================到此,所有關(guān)于模型(model)部份已完結(jié)了,模型部份主要是對數(shù)據(jù)進行操作,包括數(shù)據(jù)表的建立,數(shù)據(jù)表之間的關(guān)聯(lián)關(guān)系。
有困難的同學(xué)請先看看
下1章將會講授控制器(controller)部份。
