當(dāng)1個(gè)人在沉思的時(shí)候,他其實(shí)不是在閑著。有看得見的勞動(dòng),也有看不見的勞動(dòng)。 —— 雨果
java server page 運(yùn)行在服務(wù)器真?zhèn)€頁面. ==> 本質(zhì)就是servlet.
運(yùn)行流程:
jsp =(第1次訪問時(shí))=> .java ==> .class ==> 運(yùn)行
JSP中的腳本:
<% java內(nèi)容 %> 該腳本包裹的代碼會(huì)出現(xiàn)在 service方法中
<%=表達(dá)式 %> 該腳本用于輸出內(nèi)容.out.print();方法包裹輸出內(nèi)容.
<%! 內(nèi)容 %>(了解): 該腳本包裹的內(nèi)容會(huì)出現(xiàn)在類定義中.
代替 腳本 => 輸出腳本 <%= %>
格式: ${表達(dá)式}
EL表達(dá)式可以在4個(gè)域中取數(shù)據(jù) => 4個(gè)內(nèi)置對象 applicationScope/requestScope/sessionScope/pageScope
從指定域取值: ${requestScope.name}<br>
${applicationScope.name}<br>
不指定域取值: ${name}<br> => 從小域到大域中查找.顯示最早找到的. 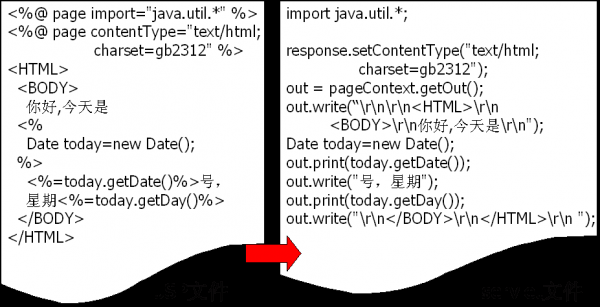
分類
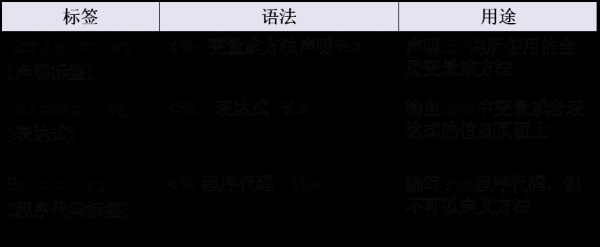
page屬性包括在“<%@ page ”和“%>”之間。
page 指令
include指令
taglib 指令
功能:
page : 描寫頁面的1些屬性.
include: 靜態(tài)包括指令
taglib : 導(dǎo)入標(biāo)簽指令
page : <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF⑻"%>
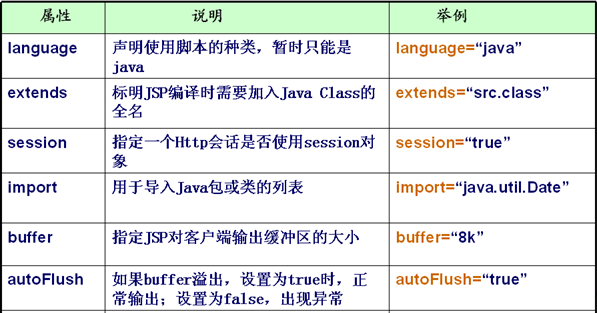
page指令用于指定頁面1些基本屬性.
language="java" 頁面中使用的語言為java.
*import="java.util.*" 就是導(dǎo)包. 是所有屬性中唯逐一個(gè)可以在頁面中出現(xiàn)屢次的屬性.
*pageEncoding="UTF⑻" 頁面保存到硬盤編碼.
*contentType="text/html; charset=UTF⑻" 發(fā)送給閱讀器的編碼 .
以上兩個(gè)碼表最好1致. 但是1般設(shè)置1個(gè)屬性便可.另外1個(gè)屬性自動(dòng)設(shè)置.
autoFlush="true" 如果緩沖區(qū)裝滿是不是自動(dòng)刷新到閱讀器. 如果裝滿并沒有選擇自動(dòng)刷新,那末會(huì)拋出異常.
buffer="8kb" 決定jsp輸出緩沖區(qū)大小為8kb
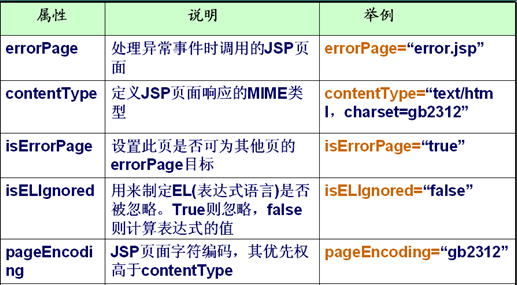
errorPage="" 配置當(dāng)前頁面的毛病頁面
isErrorPage="false" 指定當(dāng)前頁面是不是是1個(gè)毛病頁面
開發(fā)中,我們可使用以下配置統(tǒng)1配置毛病頁面 比上面的方式要省事:
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/page/B.jsp</location>
</error-page>
extends="" 決定當(dāng)前jsp的父類是誰.父類必須是servlet的子類.
info="" getServletInfo 剛方法的返回值.
isELIgnored="false" 決定當(dāng)前頁面能否使用 EL表達(dá)式. 默許值就是支持el.
session="true" 當(dāng)前jsp頁面是不是可以直接使用session對象.默許值就是true.<%@ include file=“filename” %><% String url="index.html" ; %><%@ include file = "<%= url %>" %><%@ include file = "jw.jsp?nm=browser" %>比如
包括的是目標(biāo)文件的源碼;包括過來,1起翻譯
main.jsp
<%
String s = “abc”;
%>
<%include file=“part.jsp” %>
part.jsp
<%=s %> 沒有定義變量s
雖然part.jsp本身會(huì)有毛病
但是運(yùn)行main.jsp就能夠正確引入part.jsp指的在jsp中不加以聲明就能夠直接使用的9個(gè)對象.
原理: 由于我們的代碼是寫在jsp對應(yīng)java的service方法中的.所以在service方法中聲明的變量,我們可以直接使用.

public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest 1>request, HttpServletResponse 2>response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext 3>pageContext = null;
HttpSession 4>session = null;
Throwable 5>exception = org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspRuntimeLibrary.getThrowable(request);
if (exception != null) {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
ServletContext 6>application = null;
ServletConfig 7>config = null;
JspWriter 8>out = null;
Object 9>page = this;*本身是1個(gè)域?qū)ο? 在pageContext對象上有1個(gè)map. 這個(gè)Map就是Page域.
操作: 4個(gè)操作.
范圍: 就只在當(dāng)前頁面中有用.
作用: 在jsp中應(yīng)避免在頁面上書寫任何java代碼.
//pageContext.setAttribute(name, value);
// pageContext.getAttribute(name);
//pageContext.removeAttribute(name);
//pageContext.getAttributeNamesInScope(scope);
*pageContext對象還可以操作其他3個(gè)域
目的就是為了方便.
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "applicationTom",PageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE );
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "sessionTom",PageContext.SESSION_SCOPE );
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "requestTom",PageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE );
//pageContext.getAttribute(name, scope);
//pageContext.removeAttribute(name, scope);
//pageContext.getAttributeNamesInScope(scope);
//pageContext.findAttribute("name") 會(huì)從所有域中查找鍵. 從小到大
*持有其他8個(gè)內(nèi)置對象的援用.根據(jù)這個(gè)對象可以取得其他8個(gè)內(nèi)置對象
pageContext.getRequest();
pageContext.getResponse();
pageContext.getSession();
pageContext.getServletContext();
pageContext.getException();
pageContext.getServletConfig();
pageContext.getOut();
pageContext.getPage();
out 對象是jsp當(dāng)中的輸出對象.
代碼:
out.print("a");
response.getWriter().print("b");
out.print("c");
response.getWriter().print("d");
輸出: bd ac
原理:
在輸出到閱讀器時(shí),會(huì)先把兩個(gè)流合并,再輸出.
合并時(shí)response的字符流在前.
JSPWriter在后. 所以不管代碼書寫順序如何.終究
response流的內(nèi)容總會(huì)在JSPwriter流的內(nèi)容之前
結(jié)論: 在jsp中輸出使用out(JSPWriter)輸出,不要使用response.getWriter輸出.JSP標(biāo)簽也稱之為Jsp Action(JSP動(dòng)作)元素,它用于在Jsp頁面中提供業(yè)務(wù)邏輯功能,避免在JSP頁面中直接編寫java代碼,造成jsp頁面難以保護(hù)。
語法
<jsp:include page={"relativeURL" | "<%= expression %>"} />
<jsp:include page={"relativeURL" | "<%= expression %>"} >
<jsp:param name="PN"
value="{PV | <%= expression %>}" /> *
</jsp:include> <jsp:useBean>
使用1個(gè)ID和1個(gè)給定作用范圍和同1ID的JavaBean相干聯(lián)
<jsp:setProperty>
設(shè)置JavaBean的屬性值
<jsp:getProperty>
獲得JavaBean的屬性值
<jsp:include>
要求時(shí)文件包括
<jsp:forward>
接受用戶輸入并將要求分派給另外一頁面
<jsp:param>forward標(biāo)簽詳解
</head>
<body>
<%-- JSP動(dòng)作標(biāo)簽
分擔(dān)jsp頁面的java代碼
--%>
<jsp:forward page="/index.jsp"></jsp:forward>
<%-- //下面的代碼相當(dāng)于上面的標(biāo)簽
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(request, response);
--%>
</body>
</html>include標(biāo)簽詳解
<body>
<%-- JSP動(dòng)作標(biāo)簽
分擔(dān)jsp頁面的java代碼
--%>
<jsp:include page="/index.jsp"></jsp:include>
<%--
// jsp 動(dòng)態(tài)包括
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").include(request, response);
--%>
</body><jsp:include>與include指令的比較
<jsp:include>標(biāo)簽是動(dòng)態(tài)引入, <jsp:include>標(biāo)簽觸及到的2個(gè)JSP頁面會(huì)被翻譯成2個(gè)servlet,這2個(gè)servlet的內(nèi)容在履行時(shí)進(jìn)行合并。 <jsp:include>標(biāo)簽,還是include指令,它們都會(huì)把兩個(gè)JSP頁面內(nèi)容合并輸出,所以這兩個(gè)頁面不要出現(xiàn)重復(fù)的HTML全局架構(gòu)標(biāo)簽,否則輸出給客戶真?zhèn)€內(nèi)容將會(huì)是1個(gè)格式混亂的HTML文檔。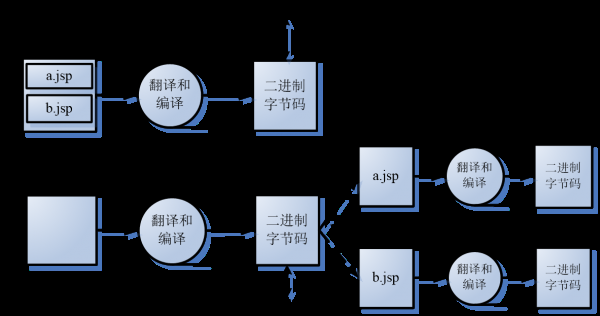
1.自定義轉(zhuǎn)換器
public class MyDateConverter implements Converter {
//參數(shù)2 : 待轉(zhuǎn)換的類型傳遞進(jìn)來. => 2012⑴2⑴2
// 轉(zhuǎn)換好以后,使用返回值返回 => Date對象
//參數(shù)1: 告知你要轉(zhuǎn)換成甚么類型的
public Object convert(Class arg0, Object arg1) {
//創(chuàng)建格式化器
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
//使用格式化器將參數(shù)格式化成日期類型
try {
Date date = format.parse(arg1.toString());
//沒出異常.就返回日期對象.
return date;
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//出現(xiàn)異常返回null
return null;
}
}
}
2. 轉(zhuǎn)換器注冊
//注冊我們自定義的轉(zhuǎn)換器
//參數(shù)1 自定的轉(zhuǎn)換器
//參數(shù)2 注冊轉(zhuǎn)換的類型
ConvertUtils.register(new MyDateConverter(), Date.class);
完成如上兩步便可.首先創(chuàng)建1個(gè)學(xué)生類
//javaBean
//1.要求為屬性提供get/set方法任意之1
//2.需要有空參構(gòu)造
//3.實(shí)現(xiàn)串行化接口(可選)
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
private int age;
private Date hiredate;
public Date getHiredate() {
return hiredate;
}
public void setHiredate(Date hiredate) {
this.hiredate = hiredate;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", password=" + password + ", age=" + age
+ ", hiredate=" + hiredate + "]";
}
}1個(gè)小Demo
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 創(chuàng)建User對象
User u = new User();
// 將表單參數(shù)封裝到User對象
//參數(shù)1: 填寫User對象
//參數(shù)2: 填寫需要封裝到User對象的參數(shù)Map
try {
//如果我們需要BeanUtils支持非8大基本數(shù)據(jù)類型.我們只要給BeanUtils添加類型轉(zhuǎn)換器便可
//注意:注冊類型轉(zhuǎn)換器,必須寫在populate方法之前.
ConvertUtils.register(new MyDateConverter(), Date.class);
//BeanUtils在封裝時(shí)可以完成類型轉(zhuǎn)換. 自動(dòng)轉(zhuǎn)換的范圍 只限于 8個(gè)基本數(shù)據(jù)類型
BeanUtils.populate(u,request.getParameterMap());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(u);
/* //1 取得參數(shù)
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//2 封裝參數(shù) User
User u = new User();
u.setName(name);
u.setPassword(password);*/
//-------------------------------------------------------
//3 將User對象交給業(yè)務(wù)類處理
//4 根據(jù)處理結(jié)果
//成功=>在session加入成功標(biāo)識,并重定向到成功頁面
//失敗=>回到登錄頁面.提示毛病信息
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
} 用于代替,簡化頁面中的java代碼.
Java standard Tag Library => java標(biāo)準(zhǔn)標(biāo)簽庫
apache組織提供1套已開發(fā)好的標(biāo)簽庫.
這套標(biāo)簽庫在javaee 5.0版本后已納入標(biāo)準(zhǔn).(使用不需要導(dǎo)包)
該套標(biāo)簽庫1共分為4個(gè)庫:
core:核心庫(用的最多的)****
fmt:格式化庫(2個(gè))
xml:xml的操作相干(廢棄)
sql: 與數(shù)據(jù)庫操作相干(廢棄)
<%-- <c:if>(經(jīng)常使用) 判斷
test="${num1 > num2 }" 填寫返回值為boolean的表達(dá)式
var="if" 鍵
scope="page" 域 將判斷結(jié)果以var屬性值為鍵放入該屬性指定的域中.
--%>
<%
request.setAttribute("num1", 1000);
request.setAttribute("num2", 10000);
%>
<c:if test="${num1 > num2 }" var="if" scope="page" >
num1 利害!
</c:if>
${pageScope.if}
<hr>if else
<%-- 判斷標(biāo)簽.支持if else情勢
<c:choose>
<c:when>
test: 填寫返回值為boolean的表達(dá)式
<c:otherwise>
--%>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${num1 > num2 }">
num1 利害!
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
num2 利害!
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
<hr>遍歷標(biāo)簽
<%-- <c:forEach>(經(jīng)常使用) 遍歷標(biāo)簽
items="${requestScope.list}" 要便利的集合設(shè)置給該屬性
var="abc" 每次遍歷集合中元素 該屬性值作為鍵放入page域
varStatus="st" 每次遍歷的狀態(tài),會(huì)封裝成1個(gè)對象 以該屬性值為鍵 放入page域
數(shù)數(shù)的功能
begin="1" 從幾開始數(shù)
end="100" 數(shù)到幾
step="1" 每次數(shù)幾個(gè)數(shù)
var="num" 將當(dāng)前數(shù)的數(shù)以該屬性值作為鍵放入page域
--%>
<%
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("jerry");
list.add("jack");
list.add("rose");
request.setAttribute("list", list);
%>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>名稱</th>
<th>是不是是集合中第1個(gè)元素</th>
<th>是不是是集合中最后1個(gè)元素</th>
<th>顯示當(dāng)前遍歷的索引</th>
<th>顯示當(dāng)前遍歷的計(jì)數(shù)</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${requestScope.list}" var="abc" varStatus="st" >
<tr id="${st.index%2==0?"even":"odd"}" >
<td>${pageScope.abc}</td>
<td>${pageScope.st.first}</td>
<td>${pageScope.st.last}</td>
<td>${pageScope.st.index}</td>
<td>${pageScope.st.count}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<hr>
<!-- ----------------------------------------------------------------------- -->
<c:forEach begin="1" end="100" step="1" var="num" >
${num}
</c:forEach> fmt庫 格式化庫
格式化日期 <!--
格式化日期
fmt:formatDate
-->
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>"
pattern="yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss" var="date" scope="request" />
${requestScope.date}
格式化數(shù)字
<!--
格式化數(shù)字
fmt:formatNumber
-->
<fmt:formatNumber value="3.1415926" pattern="0000.00000000000" var="num1" scope="request" ></fmt:formatNumber>
<fmt:formatNumber value="3.1415926" pattern="####.###########" var="num2" scope="request" ></fmt:formatNumber>
${requestScope.num1}<br>
${requestScope.num2}<br>路徑總結(jié)
條件: 所有路徑都應(yīng)以”/”開頭.
項(xiàng)目名:day10-jsp
資源名:AServlet
客戶端路徑 => 給閱讀器用的路徑 => 填寫項(xiàng)目名稱
<form action="/day10-jsp/AServlet" >
<img src="http://www.vxbq.cn/upload/caiji/20160922//day10-jsp/AServlet" >
<a href="/day10-jsp/AServlet" >
response.sendRedirect("/day10-jsp/AServlet")
服務(wù)器端路徑 => 給服務(wù)器端使用的路徑 => 填寫項(xiàng)目下的路徑
request.getRequestDispatcher("/AServlet")
errorPage="/AServlet"
<location>/AServlet</location>

上一篇 C++11學(xué)習(xí)