|
文檔版本
|
開發工具
|
測試平臺
|
工程名字
|
日期
|
作者
|
備注
|
|
V1.0
|
|
|
|
2016.06.25
|
lutianfei
|
none
|
-
內容梳理
-
第1天:基礎知識(重點,內容量多)
-
對原生態jdbc程序(單獨使用jdbc開發)問題總結
-
mybatis框架原理 (掌握)
-
mybatis入門程序
-
用戶的增、刪、改、查
-
mybatis開發dao兩種方法:
-
原始dao開發方法(程序需要編寫dao接口和dao實現類)(掌握)
-
mybaits的mapper接口(相當于dao接口)代理開發方法(掌握)
-
mybatis配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
-
mybatis核心:
-
mybatis輸入映照(掌握)
-
mybatis輸出映照(掌握)
-
mybatis的動態sql(掌握)
-
第2天:高級知識
-
定單商品數據模型分析
-
高級結果集映照(1對1、1對多、多對多)
-
mybatis延遲加載
-
mybatis查詢緩存(1級緩存、2級緩存)
-
mybaits和spring進行整合(掌握)
-
mybatis逆向工程
-
POJO : 名稱解釋
-
POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object)簡單的Java對象,實際就是普通JavaBeans,是為了不和EJB混淆所創造的簡稱。
-
使用POJO名稱是為了不和EJB混淆起來, 而且簡稱比較直接. 其中有1些屬性及其getter setter方法的類,沒有業務邏輯,有時可以作為VO(value -object)或dto(Data Transform Object)來使用.固然,如果你有1個簡單的運算屬性也是可以的,但不允許有業務方法,也不能攜帶有connection之類的方法。
原生態jdbc程序中問題總結
-
1、數據庫連接,使用時就創建,不使用立即釋放,對數據庫進行頻繁連接開啟和關閉,造成數據庫資源浪費,影響 數據庫性能。
-
2、將sql語句硬編碼到java代碼中,如果sql 語句修改,需要重新編譯java代碼,不利于系統保護。
-
假想:將sql語句配置在xml配置文件中,即便sql變化,不需要對java代碼進行重新編譯。
-
3、向preparedStatement中設置參數,對占位符號位置和設置參數值,硬編碼在java代碼中,不利于系統保護。
-
假想:將sql語句及占位符號和參數全部配置在xml中。
-
4、從resutSet中遍歷結果集數據時,存在硬編碼,將獲得表的字段進行硬編碼,不利于系統保護。
Mybatis框架
-
MyBatis 本是apache的1個開源項目iBatis, 2010年這個項目由apache software foundation 遷移到了google code,并且改名為MyBatis,實質上Mybatis對ibatis進行1些改進。
-
MyBatis是1個優秀的持久層框架,它對jdbc的操作數據庫的進程進行封裝,使開發者只需要關注 SQL 本身,而不需要花費精力去處理例如注冊驅動、創建connection、創建statement、手動設置參數、結果集檢索等jdbc復雜的進程代碼。
-
Mybatis通過xml或注解的方式將要履行的各種statement(statement、preparedStatemnt、CallableStatement)配置起來,并通過java對象和statement中的sql進行映照生成終究履行的sql語句,最后由mybatis框架履行sql并將結果映照成java對象并返回。
-
mybatis可以將向 preparedStatement中的輸入參數自動進行輸入映照,將查詢結果集靈活映照成java對象。(輸出映照)
-
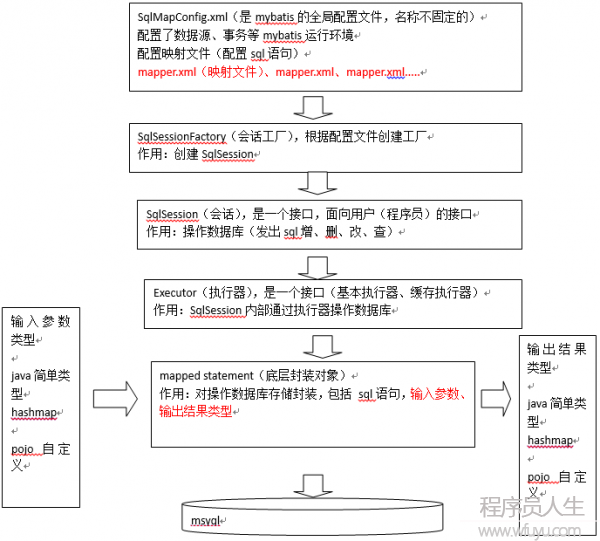
MyBatis框架示意圖
-
mapper.xml文件即sql映照文件,文件中配置了操作數據庫的sql語句。此文件需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加載。
-
通過mybatis環境等配置信息構造SqlSessionFactory即會話工廠
-
由會話工廠創建sqlSession即會話,操作數據庫需要通過sqlSession進行。
-
mybatis底層自定義了Executor履行器接口操作數據庫,Executor接口有兩個實現,1個是基本履行器、1個是緩存履行器。
-
Mapped Statement也是mybatis1個底層封裝對象,它包裝了mybatis配置信息及sql映照信息等。mapper.xml文件中1個sql對應1個Mapped Statement對象,sql的id即是Mapped statement的id。
-
Mapped Statement對sql履行輸入參數進行定義,包括HashMap、基本類型、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在履行sql前將輸入的java對象映照至sql中,輸入參數映照就是jdbc編程中對preparedStatement設置參數。
-
Mapped Statement對sql履行輸出結果進行定義,包括HashMap、基本類型、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在履行sql后將輸出結果映照至java對象中,輸出結果映照進程相當于jdbc編程中對結果的解析處理進程。
MyBatis入門程序
-
需求
-
根據用戶id(主鍵)查詢用戶信息
-
根據用戶名稱模糊查詢用戶信息
-
添加用戶
-
刪除用戶
-
更新用戶
-
3.1 環境
-
java環境:jdk1.7.0_72
-
eclipse:indigo
-
mysql:5.1
-
mybatis運行環境(jar包):
-
從 https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis⑶/releases 下載,3.2.7版本
-
lib下:依賴包
-
mybatis⑶.2.7.jar:核心包
-
mybatis⑶.2.7.pdf,操作指南
創建mysql數據庫
# Global logging configuration log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout # Console output... log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
-
工程結構

-
SqlMapConfig.xml
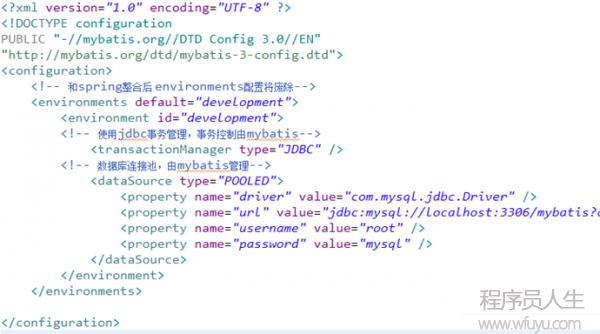
<configuration> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name= "driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name= "url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf⑻" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="mysql" /> dataSource> environment> environments> configuration>
根據用戶id(主鍵)查詢用戶信息
創建po類
-
Po類作為mybatis進行sql映照使用,po類通常與數據庫表對應,User.java以下:
Public class User { private int id; private String username; private String sex; private Date birthday; private String address; get/set... toString
映照文件
-
映照文件命名:
-
User.xml(原始ibatis命名)
-
MyBatis的mapper代理開發映照文件名稱叫XXXMapper.xml
-
比如:UserMapper.xml、ItemsMapper.xml
-
在映照文件中配置sql語句
-
在classpath下的sqlmap目錄下創建sql映照文件Users.xml:
-
namespace : 命名空間,用于隔離sql語句,后面會講另外一層非常重要的作用。
-
配置參數說明
-
id:標識 映照文件中的 sql 將sql語句封裝到mappedStatement對象中,所以將id稱為statement的id
-
parameterType:指定輸入 參數的類型,這里指定int型
-
#{}表示1個占位符號
-
#{id}:其中的id表示接收輸入 的參數,參數名稱就是id,如果輸入 參數是簡單類型,#{}中的參數名可以任意,可以value或其它名稱
-
resultType:指定sql輸出結果的所映照的java對象類型,select指定resultType表示將單條記錄映照成的java對象。
<mapper namespace="test"> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id=#{value} select>
在SqlMapConfig.xml加載映照文件
-
在sqlMapConfig.xml中加載User.xml;
-
parameterType:定義輸入到sql中的映照類型,#{id}表示使用preparedstatement設置占位符號并將輸入變量id傳到sql。
-
resultType:定義結果映照類型。
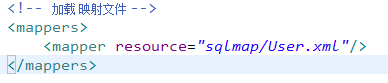
<mappers> <mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/> mappers>
測試程序編寫
public class MybatisFirst { @Test public void findUserByIdTest() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user); sqlSession.close();
}
}
根據用戶名稱模糊查詢用戶信息
映照文件
-
使用User.xml,添加根據用戶名稱模糊查詢用戶信息的sql語句。
-
resultType:指定就是單條記錄所映照的java對象 類型
-
${}:表示拼接sql串,將接收到參數的內容不加任何修飾拼接在sql中。
-
value:接收輸入參數的內容,如果傳入類型是簡單類型,{}中只能使用value
<select id="findUserByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> SELECT * FROM USER WHERE username LIKE '%${value}%' select>
程序代碼
@Test public void findUserByNameTest() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); Listlist = sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByName", "小明");
System.out.println(list);
sqlSession.close();
}
-
知識點回顧
-
#{}和${}
-
#{}表示1個占位符號,通過#{}可以實現preparedStatement向占位符中設置值,自動進行java類型和jdbc類型轉換,#{}可以有效避免sql注入。#{}可以接收簡單類型值或pojo屬性值。 如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單類型值,#{}括號中可以是value或其它名稱。
-
${}表示拼接sql串,通過${}可以將parameterType 傳入的內容拼接在sql中且不進行jdbc類型轉換,${}可以接收簡單類型值或pojo屬性值,如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單類型值,${}括號中只能是value。
-
parameterType和resultType
-
parameterType:指定輸入參數類型,mybatis通過ognl從輸入對象中獲得參數值拼接在sql中。
-
resultType:指定輸出結果類型,mybatis將sql查詢結果的1行記錄數據映照為resultType指定類型的對象。
-
selectOne和selectList
-
selectOne查詢1條記錄,如果使用selectOne查詢多條記錄則拋出異常:
-
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 3 at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectOne(DefaultSqlSession.java:70)
-
selectList可以查詢1條或多條記錄。
添加用戶
-
在 User.xml中配置添加用戶的Statement

@Test public void insertUserTest() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = new User();
user.setUsername("王小軍");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("1");
user.setAddress("河南鄭州");
sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user); sqlSession.commit(); System.out.println(user.getId()); sqlSession.close();
}
-
自增主鍵返回
-
mysql自增主鍵,履行insert提交之前自動生成1個自增主鍵。
-
通過mysql函數獲得到剛插入記錄的自增主鍵:
-
LAST_INSERT_ID()
-
是insert以后調用此函數。
-
將插入數據的主鍵返回,返回到user對象中
-
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID():得到剛insert進去記錄的主鍵值,只適用與自增主鍵
-
keyProperty:將查詢到主鍵值設置到parameterType指定的對象的哪一個屬性
-
order:SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()履行順序,相對insert語句來講它的履行順序
-
resultType:指定SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()的結果類型
-
修改insertUser定義:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer"> SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() selectKey> insert into user ( username,birthday,sex,address) value(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) insert>
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String"> SELECT uuid() selectKey> insert into user ( id,username,birthday,sex,address) value(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
SELECT 序列名.nextval()insert into user ( id,username,birthday,sex,address) value(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
刪除用戶
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer"> delete from user where id=#{id} delete>
@Test public void deleteUserTest() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUser", 39); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close();
}
更新用戶






