簡單幾步教你實現對 Drawable 的扇形區域剪切顯示
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2014-11-21 08:20:15 閱讀次數:4639次
大家如果喜歡我的博客,請關注1下我的微博,請點擊這里(http://weibo.com/kifile),謝謝
轉載請標明出處(http://blog.csdn.net/kifile),再次感謝
在開發進程中,單純的 Drawable 文件沒法滿足我們對全部項目的需求.
有時候在制作過場動畫的時候,我們會希望將1個 Drawable 文件以中心為基準,按順時針漸漸顯示出來,可是 Android 并沒有為我們提供1個工具類,我們也不希望為了單純的顯示整張圖片而去制作 N 張圖片以滿足過場動畫的需求,那末我們這個時候只能斟酌對 Drawable 的繪畫區域做裁剪,讓他只顯示扇形區域的大小,以滿足我們的需求.
幸而, Android 本身有1個 ClipDrawable 類,這個類讓我們能夠輕松的顯示進度條加載進度,本次我們也將根據這個類來創建1個類似的代碼
先送上具體源碼,然后我們會詳細分析1下裁剪顯示區域的原理
/*
* Copyright (C) 2014 Kifile(kifile@kifile.com)
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE⑵.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.kifile.graphics;
import android.content.res.ColorStateList;
import android.graphics.*;
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;
/**
* Created by kifile on 14/10/31.
*/
public class SectorDrawable extends Drawable implements Drawable.Callback {
private Drawable mDrawable;
private Path mPath = new Path();
private float mPercent;
public SectorDrawable(Drawable drawable) {
this.mDrawable = drawable;
if (drawable != null) {
drawable.setCallback(this);
}
}
@Override
public int getChangingConfigurations() {
return super.getChangingConfigurations() | mDrawable.getChangingConfigurations();
}
@Override
public boolean getPadding(Rect padding) {
return mDrawable.getPadding(padding);
}
@Override
public boolean setVisible(boolean visible, boolean restart) {
mDrawable.setVisible(visible, restart);
return super.setVisible(visible, restart);
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
mPath.reset();
RectF rect = new RectF(getBounds());
double radius = Math.pow(Math.pow(rect.right, 2) + Math.pow(rect.bottom, 2), 0.5);
mPath.moveTo(rect.right / 2, rect.bottom / 2);
mPath.lineTo(rect.right / 2, 0);
if (mPercent > 0.125f) {
mPath.lineTo(rect.right, 0);
}
if (mPercent > 0.375f) {
mPath.lineTo(rect.right, rect.bottom);
}
if (mPercent > 0.625f) {
mPath.lineTo(0, rect.bottom);
}
if (mPercent > 0.875f) {
mPath.lineTo(0, 0);
}
mPath.lineTo((float) (rect.right / 2 + radius * Math.sin(Math.PI * 2 * mPercent)),
(float) (rect.bottom / 2 - radius * Math.cos(Math.PI * 2 * mPercent)));
mPath.close();
if (mPercent >= 0 && mPercent <= 1) {
canvas.save();
canvas.clipPath(mPath);
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
canvas.restore();
}
}
@Override
public void setAlpha(int alpha) {
mDrawable.setAlpha(alpha);
}
@Override
public int getAlpha() {
return mDrawable.getAlpha();
}
@Override
public void setColorFilter(ColorFilter cf) {
mDrawable.setColorFilter(cf);
}
@Override
public void setTintList(ColorStateList tint) {
mDrawable.setTintList(tint);
}
@Override
public void setTintMode(PorterDuff.Mode tintMode) {
mDrawable.setTintMode(tintMode);
}
@Override
public int getOpacity() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mDrawable.getOpacity();
}
@Override
public boolean isStateful() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mDrawable.isStateful();
}
@Override
protected boolean onStateChange(int[] state) {
return mDrawable.setState(state);
}
@Override
protected boolean onLevelChange(int level) {
mDrawable.setLevel(level);
invalidateSelf();
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onBoundsChange(Rect bounds) {
mDrawable.setBounds(bounds);
}
@Override
public int getIntrinsicHeight() {
return mDrawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
}
@Override
public int getIntrinsicWidth() {
return mDrawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
}
/**
* 顯示的區域范圍
*
* @param percent 0至1
*/
public void setPercent(float percent) {
if (percent > 1) {
percent = 1;
} else if (percent < 0) {
percent = 0;
}
if (percent != mPercent) {
this.mPercent = percent;
invalidateSelf();
}
}
@Override
public void invalidateDrawable(Drawable who) {
final Callback callback = getCallback();
if (callback != null) {
callback.invalidateDrawable(this);
}
}
@Override
public void scheduleDrawable(Drawable who, Runnable what, long when) {
final Callback callback = getCallback();
if (callback != null) {
callback.scheduleDrawable(this, what, when);
}
}
@Override
public void unscheduleDrawable(Drawable who, Runnable what) {
final Callback callback = getCallback();
if (callback != null) {
callback.unscheduleDrawable(this, what);
}
}
}
從上面的代碼可以看出,我們使用了裝潢者模式來處理本類,首先我們在構造函數中傳入1個實際的 Drawable 對象,并將各種事務交給了 Drawable 對象進行處理,我們只負責對 draw 方法的重寫,所以我們可以好好來看看 draw 方法.
首先大家先來看1張圖:
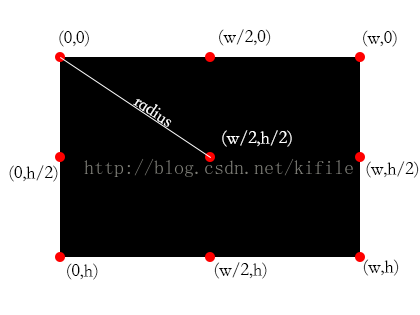
黑色部份為畫布區域, w 為寬度, h 為高度, radius 為中心點到角的距離,上圖中為我們標明了9個重要的坐標點位置,接下來我們將介紹如何根據旋轉角度來設置選定區域范圍
首先我們先規定扇形區域的起始位置為(w/2,0)處,旋轉方式為順時針旋轉,并假定有1 A 點為扇形旋轉區域另外一邊的,長度為 radius(關于 radius 的定義請參看上面) 的邊角
(1)當旋轉區域不超過1/8時,扇形區域的繪制以下:
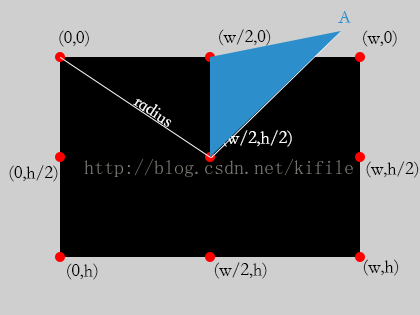
那末由圖可知,我們需要裁減的區域為上圖中的藍色區域便可
(2)對旋轉區域超過1/8,不超過3/8時,扇形區域繪制以下:
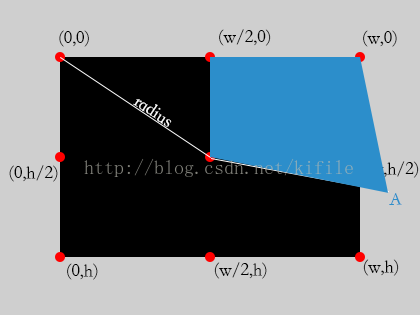
由圖可知,我們需要裁減的藍色區域,可由,中心點,起始點,右上角和 A 點連線組成
(3)對旋轉區域超過3/8不超過5/8時,扇形區域繪制以下:
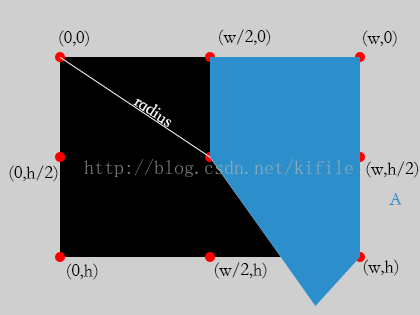
由圖可知,我們需要裁減的藍色區域,可由,中心點,起始點,右上角,右下角和 A 點連線組成
(4)對超過5/8,不超過7/8的部份,裁剪區域以下:
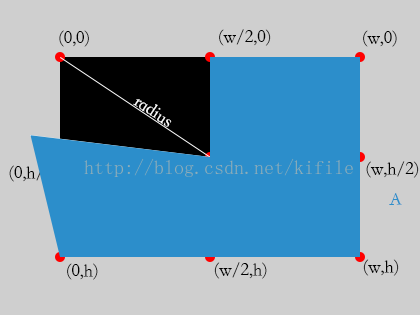
(5)對超過7/8的部份而言,裁減區域以下
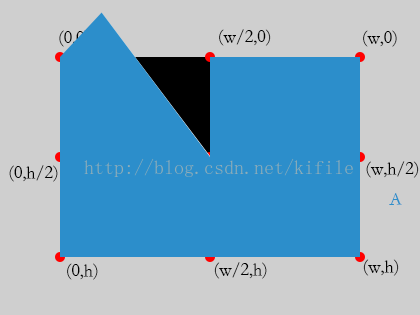
因此我們可以通過判斷設定的顯示區域,動態對畫布進行裁減,以到達顯示扇形區域的目的
具體的設置代碼,就在頂部,大家如果有興趣可以詳細看看,接下來我們將查看如何正確使用 SectorDrawable
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.sector_img);
mDrawable = new SectorDrawable(img.getDrawable());
img.setImageDrawable(mDrawable);
在這段代碼中,我們從 ImageView 中獲得了1個 Drawable 對象,然后使用 SectorDrawable 來裝潢他,然后將 setctorDrawable, 再設置到 ImageView 中
當我們需要調用代碼進行區域顯示設置時,使用
mDrawable.setPercent(percent);
詳細的1個 Activity 示例以下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2014 Kifile(kifile@kifile.com)
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE⑵.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.kifile.sample.app;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import com.kifile.graphics.SectorDrawable;
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private SectorDrawable mDrawable;
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
private float percent;
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (percent <= 1) {
percent += 0.01;
} else {
percent = 0;
return;
}
mDrawable.setPercent(percent);
Log.i("this",String.valueOf(percent));
sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 10);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.sector_img);
mDrawable = new SectorDrawable(img.getDrawable());
img.setImageDrawable(mDrawable);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
這段代碼將在點擊菜單按鈕的時候觸發事件,使用 handler 不斷刷新顯示區域,起到扇形區域顯示的目的.
好了,本次博客就到這里了,謝謝大家的翻閱
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈







