POJ 2553 The Bottom of Graph 強連通圖題解
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2014-11-20 08:45:15 閱讀次數:2618次
Description
We will use the following (standard) definitions from graph theory. Let V be a nonempty and finite set, its elements being called vertices (or nodes). Let E be a subset of the Cartesian product V×V, its elements being called edges.
Then G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Let n be a positive integer, and let p=(e1,...,en) be a sequence of length n of edges ei∈E such that ei=(vi,vi+1) for a sequence of vertices(v1,...,vn+1).
Then p is called a path from vertex v1 to vertex vn+1 in G and we say that vn+1 is reachable from v1, writing (v1→vn+1).
Here are some new definitions. A node v in a graph G=(V,E) is called a sink, if for every node w in G that is reachable from v, v is also reachable from w. The bottom of a graph is the subset of
all nodes that are sinks, i.e., bottom(G)={v∈V|?w∈V:(v→w)?(w→v)}. You have to calculate the bottom of certain graphs.
Input
The input contains several test cases, each of which corresponds to a directed graph G. Each test case starts with an integer number v, denoting the number of vertices of G=(V,E), where the vertices will be identified by the integer
numbers in the set V={1,...,v}. You may assume that 1<=v<=5000. That is followed by a non-negative integer e and, thereafter, e pairs of vertex identifiers v1,w1,...,ve,we with
the meaning that (vi,wi)∈E. There are no edges other than specified by these pairs. The last test case is followed by a zero.
Output
For each test case output the bottom of the specified graph on a single line. To this end, print the numbers of all nodes that are sinks in sorted order separated by a single space character. If the bottom is empty, print an empty line.
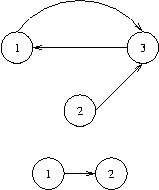
Sample Input
3 3
1 3 2 3 3 1
2 1
1 2
0
Sample Output
1 3
2
題意的本質是查找沒有出度的強連通子圖,沒有出度就是sink,the bottom of graph了。
就是利用Tarjan算法求強連通子圖,并要用標識號標識各個強連通子圖,然后記錄好各個頂點屬于哪強連通子圖。
程序帶詳細的注解:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_V = 5001;
vector<int> graAdj[MAX_V];//vector表示的鄰接圖
int conNo, vToCon[MAX_V];//強連通子圖標號及頂點對應強連通子圖號的數組
int low[MAX_V];//標識最低標識號,如果都屬于這個標識號的頂點都屬于同1連通子圖
int stk[MAX_V], top;//數組表示棧
bool vis[MAX_V];//記錄是不是訪問過的頂點
int out[MAX_V];//強連通子圖的出度,如果出度為零,那末改強連通子圖為sink
template<typename T>
inline bool equ(T t1, T t2) { return t1 == t2; }
void dfsTar(int u, int no = 1)
{
low[u] = no;//每遞歸進1個頂點,初始表示low[]
stk[++top] = u;//每一個頂點記錄入棧
vis[u] = true;//標志好是不是訪問過了
int n = (int)graAdj[u].size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int v = graAdj[u][i];
if (!vis[v])
{
dfsTar(v, no+1);//這里遞歸
if (low[u] > low[v]) low[u] = low[v];//更新最低標識號
}
else if (!vToCon[v] && low[u] > low[v]) low[u] = low[v];//更新
}
if (equ(low[u], no))//最低標識號和遞歸進的初始號相同就找到1個子圖了
{
++conNo;
int v;
do
{
v = stk[top--];//出棧
vToCon[v] = conNo;//頂點對應到子圖號
} while (v != u);//出棧到本頂點,那末改子圖所有頂點出棧終了
}
}
void Tarjan(int n)
{
conNo = 0;//記得前期的清零工作
fill(vToCon, vToCon+n+1, 0);
fill(low, low+n+1, 0);
fill(vis, vis+n+1, false);
top = ⑴;
for (int u = 1; u <= n; u++) if (!vis[u]) dfsTar(u);
}
int main()
{
int V, E, u, v;
while(~scanf("%d %d", &V, &E) && V)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++)
{
graAdj[i].clear();//清零
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
graAdj[u].push_back(v);//建立vector表示的鄰接表
}
Tarjan(V);
fill(out, out+conNo+1, 0);
for (int u = 1; u <= V; u++)
{
int n = graAdj[u].size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int v = graAdj[u][i];
if (vToCon[u] != vToCon[v])
{
out[vToCon[u]]++;//記錄強連通子圖號的出度數
}
}
}
for (int u = 1; u <= V; u++)//出度為零,即為答案:Graph Bottom
{
if (!out[vToCon[u]]) printf("%d ", u);
}
putchar('
');
}
return 0;
}
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈


