編譯nodejs及其源碼研究
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2014-11-13 09:00:57 閱讀次數:3520次
本文將從 源碼 研究nodejs 的原理、本質,探討nodejs的利用場景,和高性能開發實踐指南。
目錄:
第1節:編譯node.js
第2節:源碼分析
進入主題:以下是在win7 64 下進行,其他平臺編譯 ,請參見官網。
第1節:編譯node.js,進程很簡單
1、下載源碼。 git clone https://github.com/joyent/node
如果沒有安裝git客戶端,可以在打開https://github.com/joyent/node 點擊 Download ZIP,進行下載
2、安裝 Python 2.6 or 2.7 和 Visual Studio 2010 or 2012,我這里是 Python
2.7.8 和 Visual Studio 2012
3、進入node目錄
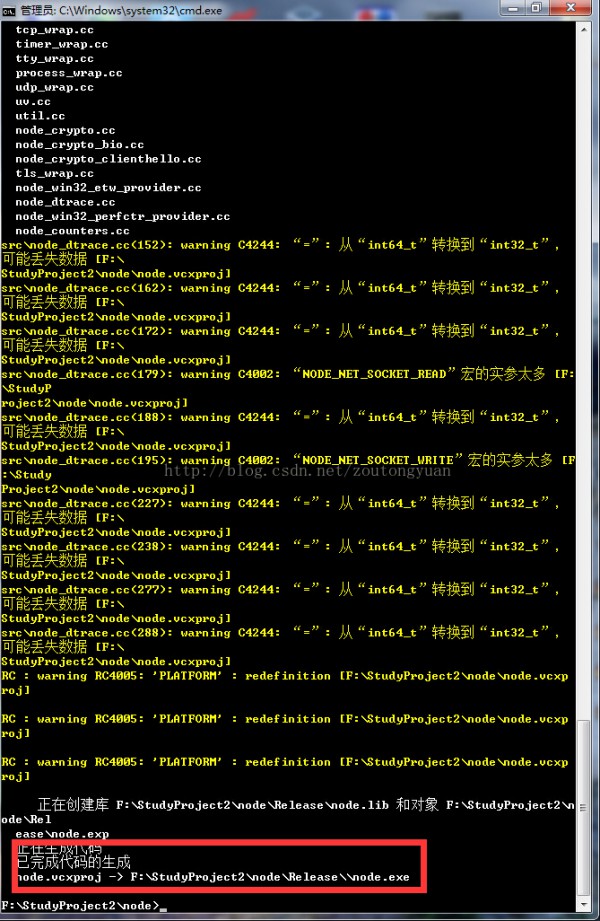
履行 vcbuild release
大概
10多分鐘 就能夠編譯成功,在Release目錄下會生成node.exe。下面是我編譯成功的圖。
第2節:源碼分析
我們在IDE 中 打開剛才的node目錄,方便我們看源碼。我這里是Idea查看。
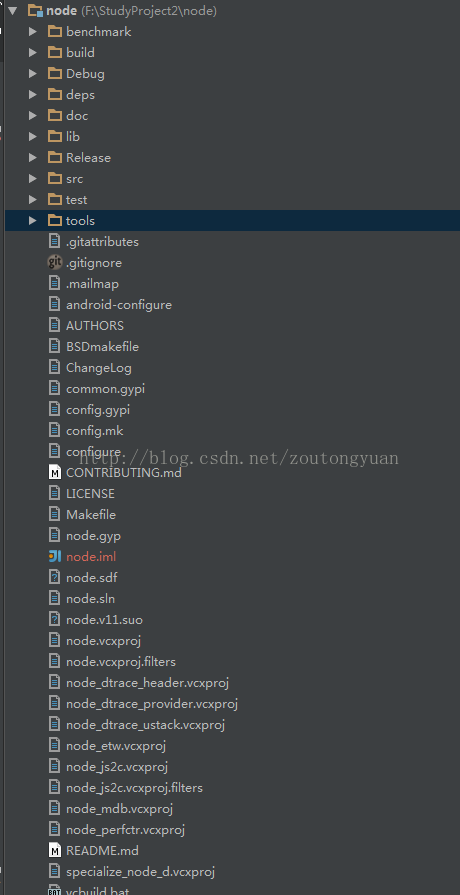
benchmark : 1些nodejs 性能測試 代碼
build:編譯nodejs 生成目錄
Debug:編譯nodejs 生成目錄
Release:編譯nodejs 生成目錄
deps:nodejs依賴 的工具包,包括 v8、http_parser、opensslzlib、zlib、uv。。。
doc:文檔
lib:包括JavaScript源碼
src:包括C++源碼
test:測試代碼
tools:編譯時用到的工具
這里我們只需關注 src 和lib 文件夾。
1、從node.cc 文件 看 node進程 啟動進程的
int Start(int argc, char** argv) {
const char* replaceInvalid = getenv("NODE_INVALID_UTF8");
if (replaceInvalid == NULL)
WRITE_UTF8_FLAGS |= String::REPLACE_INVALID_UTF8;
#if !defined(_WIN32)
// Try hard not to lose SIGUSR1 signals during the bootstrap process.
InstallEarlyDebugSignalHandler();
#endif
assert(argc > 0);
// Hack around with the argv pointer. Used for process.title = "blah".
argv = uv_setup_args(argc, argv);
// This needs to run *before* V8::Initialize(). The const_cast is not
// optional, in case you're wondering.
int exec_argc;
const char** exec_argv;
Init(&argc, const_cast<const char**>(argv), &exec_argc, &exec_argv);
#if HAVE_OPENSSL
// V8 on Windows doesn't have a good source of entropy. Seed it from
// OpenSSL's pool.
V8::SetEntropySource(crypto::EntropySource);
#endif
int code;
V8::Initialize();
{
Locker locker(node_isolate);
Isolate::Scope isolate_scope(node_isolate);
HandleScope handle_scope(node_isolate);
Local<Context> context = Context::New(node_isolate);
Environment* env = CreateEnvironment(
node_isolate, context, argc, argv, exec_argc, exec_argv);
// Assign env to the debugger's context
if (debugger_running) {
HandleScope scope(env->isolate());
env->AssignToContext(v8::Debug::GetDebugContext());
}
// This Context::Scope is here so EnableDebug() can look up the current
// environment with Environment::GetCurrent().
// TODO(bnoordhuis) Reorder the debugger initialization logic so it can
// be removed.
{
Context::Scope context_scope(env->context());
bool more;
do {
more = uv_run(env->event_loop(), UV_RUN_ONCE);
if (more == false) {
EmitBeforeExit(env);
// Emit `beforeExit` if the loop became alive either after emitting
// event, or after running some callbacks.
more = uv_loop_alive(env->event_loop());
if (uv_run(env->event_loop(), UV_RUN_NOWAIT) != 0)
more = true;
}
} while (more == true);
code = EmitExit(env);
RunAtExit(env);
}
env->Dispose();
env = NULL;
}
CHECK_NE(node_isolate, NULL);
node_isolate->Dispose();
node_isolate = NULL;
V8::Dispose();
delete[] exec_argv;
exec_argv = NULL;
return code;
}
Environment* CreateEnvironment(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<Context> context,
int argc,
const char* const* argv,
int exec_argc,
const char* const* exec_argv) {
HandleScope handle_scope(isolate);
Context::Scope context_scope(context);
Environment* env = Environment::New(context);
uv_check_init(env->event_loop(), env->immediate_check_handle());
uv_unref(
reinterpret_cast<uv_handle_t*>(env->immediate_check_handle()));
uv_idle_init(env->event_loop(), env->immediate_idle_handle());
// Inform V8's CPU profiler when we're idle. The profiler is sampling-based
// but not all samples are created equal; mark the wall clock time spent in
// epoll_wait() and friends so profiling tools can filter it out. The samples
// still end up in v8.log but with state=IDLE rather than state=EXTERNAL.
// TODO(bnoordhuis) Depends on a libuv implementation detail that we should
// probably fortify in the API contract, namely that the last started prepare
// or check watcher runs first. It's not 100% foolproof; if an add-on starts
// a prepare or check watcher after us, any samples attributed to its callback
// will be recorded with state=IDLE.
uv_prepare_init(env->event_loop(), env->idle_prepare_handle());
uv_check_init(env->event_loop(), env->idle_check_handle());
uv_unref(reinterpret_cast<uv_handle_t*>(env->idle_prepare_handle()));
uv_unref(reinterpret_cast<uv_handle_t*>(env->idle_check_handle()));
if (v8_is_profiling) {
StartProfilerIdleNotifier(env);
}
Local<FunctionTemplate> process_template = FunctionTemplate::New(isolate);
process_template->SetClassName(FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "process"));
Local<Object> process_object = process_template->GetFunction()->NewInstance();
env->set_process_object(process_object);
SetupProcessObject(env, argc, argv, exec_argc, exec_argv);
Load(env);
return env;
}
void SetupProcessObject(Environment* env,
int argc,
const char* const* argv,
int exec_argc,
const char* const* exec_argv) {
HandleScope scope(env->isolate());
Local<Object> process = env->process_object();
process->SetAccessor(env->title_string(),
ProcessTitleGetter,
ProcessTitleSetter);
// process.version
READONLY_PROPERTY(process,
"version",
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), NODE_VERSION));
// process.moduleLoadList
READONLY_PROPERTY(process,
"moduleLoadList",
env->module_load_list_array());
// process.versions
Local<Object> versions = Object::New(env->isolate());
READONLY_PROPERTY(process, "versions", versions);
const char http_parser_version[] = NODE_STRINGIFY(HTTP_PARSER_VERSION_MAJOR)
"."
NODE_STRINGIFY(HTTP_PARSER_VERSION_MINOR);
READONLY_PROPERTY(versions,
"http_parser",
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), http_parser_version));
// +1 to get rid of the leading 'v'
READONLY_PROPERTY(versions,
"node",
OneByteString(env->isolate(), NODE_VERSION + 1));
READONLY_PROPERTY(versions,
"v8",
OneByteString(env->isolate(), V8::GetVersion()));
READONLY_PROPERTY(versions,
"uv",
OneByteString(env->isolate(), uv_version_string()));
READONLY_PROPERTY(versions,
"zlib",
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), ZLIB_VERSION));
const char node_modules_version[] = NODE_STRINGIFY(NODE_MODULE_VERSION);
READONLY_PROPERTY(
versions,
"modules",
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), node_modules_version));
void Load(Environment* env) {
HandleScope handle_scope(env->isolate());
// Compile, execute the src/node.js file. (Which was included as static C
// string in node_natives.h. 'natve_node' is the string containing that
// source code.)
// The node.js file returns a function 'f'
atexit(AtExit);
TryCatch try_catch;
// Disable verbose mode to stop FatalException() handler from trying
// to handle the exception. Errors this early in the start-up phase
// are not safe to ignore.
try_catch.SetVerbose(false);
Local<String> script_name = FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), "node.js");
Local<Value> f_value = ExecuteString(env, MainSource(env), script_name);
if (try_catch.HasCaught()) {
ReportException(env, try_catch);
exit(10);
}
assert(f_value->IsFunction());
Local<Function> f = Local<Function>::Cast(f_value);
// Now we call 'f' with the 'process' variable that we've built up with
// all our bindings. Inside node.js we'll take care of assigning things to
// their places.
// We start the process this way in order to be more modular. Developers
// who do not like how 'src/node.js' setups the module system but do like
// Node's I/O bindings may want to replace 'f' with their own function.
// Add a reference to the global object
Local<Object> global = env->context()->Global();
大致的進程是這樣的 :
加載 V8 、OpenSSL ...
創建 Environment 環境
設置 Process 進程對象
履行 node.js 文件
2、從 node.js 文件 看 global 配置進程,吐槽1下,nodejs的源碼寫的太搓了,C系語言誕生的風格?
這個文件大致是 是配置 全局變量、配置process、定義模塊對象。
后面將深入 講授
node.js 這個文件 、和結合 src 的C++類,與lib 下的 js代碼 講授nodejs。
我們可以得出1個結論: nodejs = node API + V8;

生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈




