Explain
紅黑樹是每個節點都帶有顏色屬性的二叉查找樹,顏色為紅色或黑色。在二叉查找樹強制一般要求以外,對于任何有效的紅黑樹我們增加了如下的額外要求:
性質1. 節點是紅色或黑色。
性質2. 根是黑色。
性質3. 所有葉子都是黑色(葉子是NIL節點)。
性質4. 每個紅色節點的兩個子節點都是黑色。(從每個葉子到根的所有路徑上不能有兩個連續的紅色節點)
性質5. 從任一節點到其每個葉子的所有簡單路徑都包含相同數目的黑色節點。
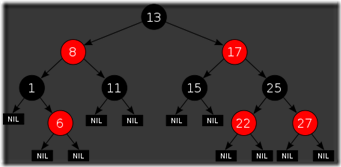
這些約束強制了紅黑樹的關鍵性質: 從根到葉子的最長的可能路徑不多于最短的可能路徑的兩倍長(性質4 保證了路徑最長的情況為一紅一黑,最短的情況為全黑,再結合性質5,可以推導出)。結果是這個樹大致上是平衡的。因為操作比如插入、刪除和查找某個值的最壞情況時間都要求與樹的高度成比例,這個在高度上的理論上限允許紅黑樹在最壞情況下都是高效的,而不同于普通的二叉查找樹。
紅黑樹結構定義:
/* * RBTree.h * * Created on: Sep 25, 2014 * Author: root */ #ifndef RBTREE_H_ #define RBTREE_H_ typedef unsigned long rbtree_key_t; typedef long rbtree_key_int_t; struct rbtree_node_t { rbtree_key_t key; //key rbtree_node_t *left; //左子樹 rbtree_node_t *right; //右子樹 rbtree_node_t *parent; //父節點 unsigned char color; //顏色 }; struct rbtree_t { rbtree_node_t *root; //根節點 rbtree_node_t *sentinel; //哨兵 }; #endif /* RBTREE_H_ */
二、樹的旋轉知識
1.左旋
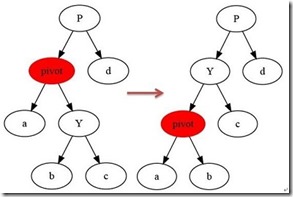
如上圖所示:
當在某個結點pivot上,做左旋操作時,我們假設它的右孩子y不是NIL[T],pivot可以為樹內任意右孩子而不是NIL[T]的結點。
左旋以pivot到y之間的鏈為“支軸”進行,它使y成為該孩子樹新的根,而y的左孩子b則成為pivot的右孩子。
偽代碼圖解:

實現代碼:
void RBTree::rbtree_left_rotate( rbtree_node_t* node_x) { rbtree_node_t *node_y; rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_y = node_x-> right; //Setp 1. 設置y node_x-> right = node_y-> left; //Step 2 .將y 的左子樹變為x的右子樹 if(node_y-> left != sentinel) { node_y-> left-> parent = node_x; } node_y-> parent = node_x-> parent; //Step 3. 設置y的父親 if(node_x == *root) //空樹,將y設為根 { *root = node_y; } else if(node_x == node_x->parent ->left ) //x為左子樹,將y放在x父節點的左子樹 { node_x-> parent-> left = node_y; } else //x為右子樹,將y放在x父節點的右子樹 { node_x-> parent-> right = node_y; } node_y-> left = node_x; //Step4.將x鏈到y的左子樹 node_x-> parent = node_y; }
2.右旋
偽代碼圖解:

實現代碼:
void rb_tree::rbtree_right_rotate( rbtree_node_t *node_x) { rbtree_node_t *node_y; rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_y = node_x-> left; //Step 1. 設置y node_x-> left = node_y-> right; //Step 2.將y的右子樹變為x的左子樹 if( node_y-> right != sentinel) { node_y-> right-> parent = node_x; } node_y-> parent = node_x-> parent; if( node_x == *root) //Step 3.若x為根,設置y為跟 { *root = node_y; } else if( node_x == node_x->parent ->right ) //x在右子樹,y設置在右子樹 { node_x-> parent-> right = node_y; } else //x在左子樹,y設置在左子樹 { node_x-> parent-> left = node_y; } node_y-> right = node_x; //Step 4.將x鏈接在y的右子樹 node_x-> parent = node_y; }
三、紅黑樹的插入
紅黑樹的插入和二叉樹的相似,都是如果左子樹小,向左子樹搜索,否則向右子樹搜索,不同的紅黑樹插入完需要調整,恢復紅黑樹的特性,偽代碼如下 :
RB-INSERT(T,z) y <- NIL[T] //Step 1.將y設置為哨兵,將x設置為根 x <- root[T] while x!=NIL[T] //Step 2.搜索,如果z比x小,向左子樹搜索,否則向右子樹搜索,y插入位置 do y <- x if key[z] < key[x] then x <- left[x] else x <- right[x] p[z] <- y if y=NIL[T] //Step 3.若為空樹,z為根, then root[T] <- z else if key[z] < key[y] //若z比y小,z放在y的左子樹 then left[y] <- z else right[y] <- z //否則,z放在y的右子樹 left[z] <- NIL[T] right[z] <- NIL[T] //Step 4.將z左右子樹設置為哨兵,顏色設置為紅色 color[z] <- RED RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T,z) //Step 5.紅黑樹調整
實現代碼:
void RBTree::rbtree_insert( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t *node_y = m_rbtree. sentinel; //Step 1.將y設置為哨兵,將x設置為根 rbtree_node_t *node_x = m_rbtree.root; if(m_rbtree.root== m_rbtree. sentinel) //若為空樹,z為根, { node_z-> parent = NULL; node_z-> left = m_rbtree. sentinel; node_z-> right = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbt_black(node_z); m_rbtree.root = node_z; return; } for(;node_x != m_rbtree.sentinel;) //Step 2.搜索,如果z比x小,向左子樹搜索,否則向右子樹搜索,y插入位置 { node_y = node_x; node_x = node_z->key - node_x->key < 0 ? node_x->left:node_x->right; } node_z->parent = node_y; if(node_z->key - node_y->key < 0) //Step 3 若z比y小,z放在y的左子樹 { node_y->left = node_z; } else //否則,z放在y的右子樹 { node_y->right = node_z; } node_z-> left = m_rbtree. sentinel; //Step 4.將z左右子樹設置為哨兵,顏色設置為紅色 node_z-> right = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbt_red(node_z); //re-balance tree rbtree_insert_fixup(node); //Step 5.紅黑樹調整 }
紅黑樹插入調整偽代碼:
RB-INSERT-FIXUP(T,z) while color[p[z]]=RED do if p[z]=left[p[p[z]]] then y <- right[p[p[z]]] if color[y]=RED then color[y] <- BLACK //情況1,z的叔叔y是紅色 color[p[z]] <- BLACK color[p[p[z]]] <- RED z <- p[p[z]] else if z=right[p[z]] //情況2,z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子 then z <- p[z] LEFT-ROTATE(T,z) color[p[z]] <- BLACK // 情況3,z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子 color[p[p[z]]] <- RED RIGHT-ROTATE(T,p[p[z]]) else (same as then clause with “right” and “left” exchanged) color[root[T]] <- BLACK
情況1:z的叔叔y是紅色
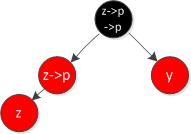
違反性質4,z和z的父親都是紅色。
調整方法:
首先將z->p涂黑,再將z->p->p涂紅,最后將y涂黑。將z->p的顏色和z->p->p的顏色對換一下,再將y涂黑,其實是把z->p->p的黑色分發到兩個紅色兒子結點中,而其自身變為紅色,維持了性質5,即維護了所有路徑黑結點數量的一致性。這里要提出的一個小細節是,紅色結點變黑色不用考慮結點顏色沖突,而黑色結點變紅色則要考慮結點顏色沖突,紅變黑,隨意變,黑變紅,看沖突(不考慮性質5的前提下)。因為z->p->p是由黑色變紅的,這時將z指向z->p->p,如果不出現結點顏色沖突的情況則完成修復,有顏色沖突則進入下一輪循環。
情況2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子
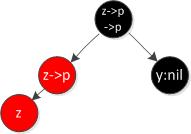
違反性質4,z和z的父親都是紅色。
調整方法:
首先也是將z->p涂黑,z->p->p涂紅,這時候,我們就會發現根結點到y結點路徑中的黑結點數目減少了1,我們再回顧一下前面對左旋、右旋方法的介紹,那么我們會發現,左旋、右旋的意義就在于此了:RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)后,為根結點到y結點的路徑上增加了一個黑色結點z->p,為根結點到z結點的路徑上減少了一個紅色結點z->p->p,一條路徑增加黑色結點,另一條路徑減少紅色結點,insert就這樣被修復了。
情況3:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子
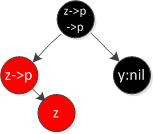
違反性質4,z和z的父親都是紅色。
調整方法:
將z->p涂黑,z->p->p涂紅,這時候,想對紅黑樹進行修復的話,你會想到什么呢?和case 3一樣直接RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)么,如果直接RIGHT-ROTATE(T,z->p->p)的話,紅色結點z將變成紅色結點z->p->p的左兒子,其實是做了無用功。那我們就想辦法把它變成case 3的那種形式吧,LEFT-ROTATE(T,z),很容易想到吧,LEFT-ROTATE(T,z)之后z,z->p,z->p->p又變成了我們喜聞樂見的三點一線的形式,也就是case 3。
實現代碼:
void RBTree::rbtree_insert_fixup( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t **root = & m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *node_y; while( node_z != *root && rbt_is_red(node_z-> parent)) { if(node_z-> parent == node_z->parent->parent->left) { node_y = node_z->parent->parent->right; //case1:z的叔叔y是紅色 if(rbt_is_red(node_y)) { rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_black(node_y); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); node_z = node_z ->parent ->parent ; } else { //case2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是右孩子 if(node_z == node_z->parent->right) { node_z = node_z ->parent ; rbtree_left_rotate( node_z); } rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); rbtree_right_rotate( node_z); } } else { node_y = node_z->parent->parent->left; //case1:z的叔叔y是紅色 if(rbt_is_red(node_y)) { rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_black(node_y); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); node_z = node_z ->parent ->parent ; } else { //case2:z的叔叔y是黑色,且z是左孩子 if(node_z == node_z->parent->left) { node_z =node_z ->parent ; rbtree_right_rotate( node_z); } rbt_black( node_z->parent); rbt_red( node_z->parent->parent); rbtree_left_rotate( node_z->parent->parent); } } } rbt_black(*root); }
四、紅黑樹的刪除
刪除的節點按照兒子的個數可以分為三種:
OK,回到紅黑樹上來。算法導論一書,給的紅黑樹結點刪除的算法實現是:
RB-DELETE(T, z) if left[z] = nil[T] or right[z] = nil[T] //沒有或者有一個兒子 then y ← z else y ← TREE-SUCCESSOR(z) //有兩個兒子,取左子樹的最大節點或右子樹的最小節點 if left[y] ≠ nil[T] then x ← left[y] else x ← right[y] p[x] ← p[y] if p[y] = nil[T] //要刪除的為根角點,則直接用x替代根節點 then root[T] ← x else if y = left[p[y]] //要刪除的節點在左子樹,則x放在在左子樹 then left[p[y]] ← x else right[p[y]] ← x //要刪除的節點在右子樹,則x放在在右子樹 if y ≠ z //z有兩個兒子 then key[z] ← key[y] //將y的數據給z,實際上是刪除的右子樹的最小節點,然后把這個節點的數據拷到了z的位置 copy y's satellite data into z if color[y] = BLACK //設置y的顏色為黑色 then RB-DELETE-FIXUP(T, x) return y
實現代碼:
void RBTree::rbtree_delete( rbtree_node_t *node_z) { rbtree_node_t **root =& m_rbtree. root; rbtree_node_t *sentinel = m_rbtree. sentinel; rbtree_node_t *node_y; //the node to replace node_z rbtree_node_t *node_x; //node_y's child bool is_node_y_red = false; if(node_z-> left == sentinel) { node_x = node_z-> right; node_y = node_z; } else if(node_z->right == sentinel) { node_x = node_z-> left; node_y = node_z; } else { node_y = rbtree_min(node_z-> right); if(node_y->left != sentinel) { node_x = node_y-> left; } else { node_x = node_y-> right; } } //the node to delete is root if(node_y == *root) { *root = node_x; rbt_black(node_x); node_z->left = NULL; node_z->right = NULL; node_z->parent = NULL; node_z->key = 0; return; } is_node_y_red = rbt_is_red(node_y); //Link node_y's child node_x to node_y's parent if(node_y == node_y-> parent-> left) { node_y-> parent-> left = node_x; } else { node_y-> parent-> right = node_x; } if(node_y == node_z) { node_x-> parent = node_y-> parent; } else { if(node_y->parent == node_z) { node_x-> parent = node_y; } else { node_x-> parent = node_y-> parent; } //replace node_z with node_y,include color,so the place of node_z is not change node_y-> left = node_z-> left; node_y-> right = node_z-> right; node_y-> parent = node_z-> parent; rbt_copy_color(node_y,node_z); //the node to delete is root if( node_z == *root) { *root = node_y; } else { if(node_z == node_z->parent ->left ) { node_z-> parent-> left = node_y; } else { node_z-> parent-> right = node_y; } } if(node_z->left != sentinel) { node_y-> left-> parent = node_y; } if(node_z->right != sentinel) { node_y-> right-> parent = node_y; } } node_z->left = NULL; node_z->right = NULL; node_z->parent = NULL; node_z->key = 0; //if node_y is a black node,the action move node_y to replace node_z change the struct of rbtree if(!is_node_y_red) { rbtree_delete_fixup(node_x); } }
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈
