C++簡易list
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2014-09-09 22:16:39 閱讀次數:2895次
list不同于vector,每個節點的結構需要自行定義,迭代器屬于雙向迭代器(不是隨即迭代器),也需要自行定義。和通用迭代器一樣,list的迭代器需要實現的操作有:++、--、*、->、==、!=。節點的數據結構命名為list_node,迭代器的數據結構命名為list_iterator。list中對迭代器的操作不應該使用算數運算,如+2、-3這樣的操作,只應該使用++、--來移動迭代器。STI版本的STL使用了一個環形list,list.end()指向一個空白節點(不存放數據)作為尾節點,空白節點的next指針指向第一個節點,空白節點的prev指針指向最后一個節點,這樣就能方便的實現begin()和end()操作,當list為空時,空白節點的next和prev均指向自己。這樣的設計是很巧妙的,省去了很多插入、刪除操作時需要考慮的邊界條件。
#ifndef __MYLIST_H__
#define __MYLIST_H__
// list節點
template <class Type>
class list_node {
public:
list_node<Type> *prev;
list_node<Type> *next;
Type data;
};
// list迭代器
template <class Type>
class list_iterator {
public:
// 迭代器必須定義的五個相應類型
typedef Type value_type;
typedef Type* pointer;
typedef Type& reference;
typedef size_t difference_type;
typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
list_iterator() : node(NULL)
{}
list_iterator(list_node<Type> *x) : node(x)
{}
list_iterator(const list_iterator<Type> &x) : node(x.node)
{}
// 成員函數盡量加const
bool operator== (const list_iterator<Type> &rhs) const
{
return node == rhs.node;
}
bool operator!= (const list_iterator<Type> &rhs) const
{
return !(operator==(rhs)); // 調用現有函數,好的策略
}
// 對迭代器接引用返回指向數據的引用
reference operator* () const
{
return node->data;
}
pointer operator-> () const
{
return &(operator*()); // 調用現有函數,好的策略
}
list_iterator& operator++ ()
{
node = node->next;
return *this;
}
list_iterator operator++ (int)
{
list_iterator<Type> old = *this;
++(*this);
return old;
}
list_iterator& operator-- ()
{
node = node->prev;
return *this;
}
list_iterator operator-- (int)
{
list_iterator<Type> old = *this;
--(*this);
return old;
}
// 迭代器通過這個指針與某個節點相聯系
list_node<Type> *node;
};
// list數據結構,SGI中的list是一個環形鏈表,這里相同
// list內部使用list_node訪問每一個保存數據的節點,對外則返回給用戶一個list_iterator迭代器,這是需要注意的
template <class Type>
class List {
public:
typedef list_iterator<Type> iterator; // iterator類型是每個容器必備的,應該盡早定義它
typedef size_t size_type;
// 構造函數
List()
{
node = get_node();
// 前后指針都指向自己,表示此list為空
node->next = node;
node->prev = node;
}
iterator begin()
{
return (list_iterator<Type>)node->next;
}
iterator end()
{
return (list_iterator<Type>)node;
}
bool empty()
{
return node->next == node; // 參見默認構造函數
}
size_type size()
{
size_type len = 0;
distance(begin(), end(), len);
return len;
}
Type& front()
{
return *begin();
}
Type& back()
{
return *(--end());
}
// 插入操作
iterator insert(iterator position, const Type &value)
{
list_node<Type> *newNode = create_node(value);
newNode->next = position.node;
newNode->prev = position.node->prev;
position.node->prev->next = newNode;
position.node->prev = newNode;
return (iterator)newNode; // 顯示類型轉換
}
void push_back(const Type &value)
{
insert(end(), value);
}
void push_front(const Type &value)
{
insert(begin(), value);
}
// 刪除操作
iterator erase(iterator position)
{
list_node<Type> *next = position.node->next;
list_node<Type> *prev = position.node->prev;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
destroy_node(position.node);
return (iterator)next;
}
void pop_back()
{
iterator tmp = end();
erase(--tmp);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
// 清除所有節點
void clear()
{
list_node<Type> *pnode = node->next;
while (pnode != node)
{
list_node<Type> *tmp = pnode->next;
destroy_node(pnode);
pnode = tmp;
}
node->next = node;
node->prev = node;
}
// 刪除值為value的所有節點
void remove(const Type &value)
{
// 為了使用上面的erase,這里定義iterator而不是list_node
iterator first = begin();
iterator last = end();
while (first != last)
{
iterator next = first;
++next;
if (*first == value)
erase(first);
first = next;
}
}
private:
// 分配一個節點
list_node<Type>* get_node()
{
return alloc.allocate(1);
}
// 釋放一個節點
void put_node(list_node<Type> *p)
{
alloc.deallocate(p, 1);
}
// 分配并構造一個節點
list_node<Type>* create_node(const Type &value)
{
list_node<Type> *p = get_node();
alloc.construct(&(p->data), value);
return p;
}
// 析構并釋放一個節點
void destroy_node(list_node<Type> *p)
{
alloc.destroy(&(p->data));
put_node(p);
}
private:
list_node<Type> *node; // 空白節點,指向list.end()
static std::allocator< list_node<Type> > alloc; // 空間配置器
};
// 類中的靜態成員一定要記得在類外定義,否則鏈接時會出錯
template <class Type>
std::allocator< list_node<Type> > List<Type>::alloc;
#endif
析構函數忘記寫了,這里補上:
~List()
{
clear();
if (node != NULL)
delete node;
}
測試代碼:
int main()
{
List<int> l;
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(4);
l.push_back(5);
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 1 2 3 4 5
List<int>::iterator iter = find(l.begin(), l.end(), 3);
iter = l.erase(iter);
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 1 2 4 5
l.insert(iter, 123);
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 1 2 123 4 5
l.push_front(0);
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 0 1 2 123 4 5
l.pop_back();
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 0 1 2 123 4
l.pop_front();
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// 1 2 123 4
l.clear();
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
// null
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_front(4);
l.push_front(5);
l.push_front(6);
l.remove(1);
l.remove(2);
l.remove(3);
l.remove(5);
copy(l.begin(), l.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
運行結果:
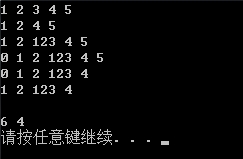
參考:
《STL源碼剖析》
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈


